Product and user experience (UX) design are both prominent fields—and make rewarding career choices. People often use the two terms interchangeably in conversation, but they’re not the same. Product designer vs. UX designer isn’t a simple “either-or” scenario—and each role has got unique responsibilities and focal points that contribute in different ways to a brand’s end product. Stay tuned to find out the differences between a UX designer and a product designer so you know their roles, responsibilities, skills, tools, and more and see which might be a more compelling calling for you.
What is a Product Designer?
A product designer is someone who leads—or who’s part of—the team that creates a new product or makes an existing one better. They take care of the entire design process for that. A product designer is a professional who works in cross-functional teams to address technical constraints and ensure usability is well in place from ideation to production. The contribution they make to the overall product experience goes far beyond its visual appeal.
"Our role is to imagine products that don't exist and guide them to life."
– Apple designer Christopher Stringer
Learn more about product design in our guide | What is Product Design?
What are Responsibilities and Job Duties of a Product Designer?
They translate their firm grasp of those needs into functional and appealing designs. However, it’s not a solo affair, as they collaborate with cross-functional teams to bring their designs to life and the best possible—or most improved—end product to show for it.
Product designers take on the task of understanding user needs and user behavior—which is why one of their main activities is to conduct user research and create user personas to understand their needs and motivations. A product designer might use interviews, surveys, questionnaires, diary studies, secondary market research data, or many other tools and resources to understand the users and the business context of the product they’re working on.
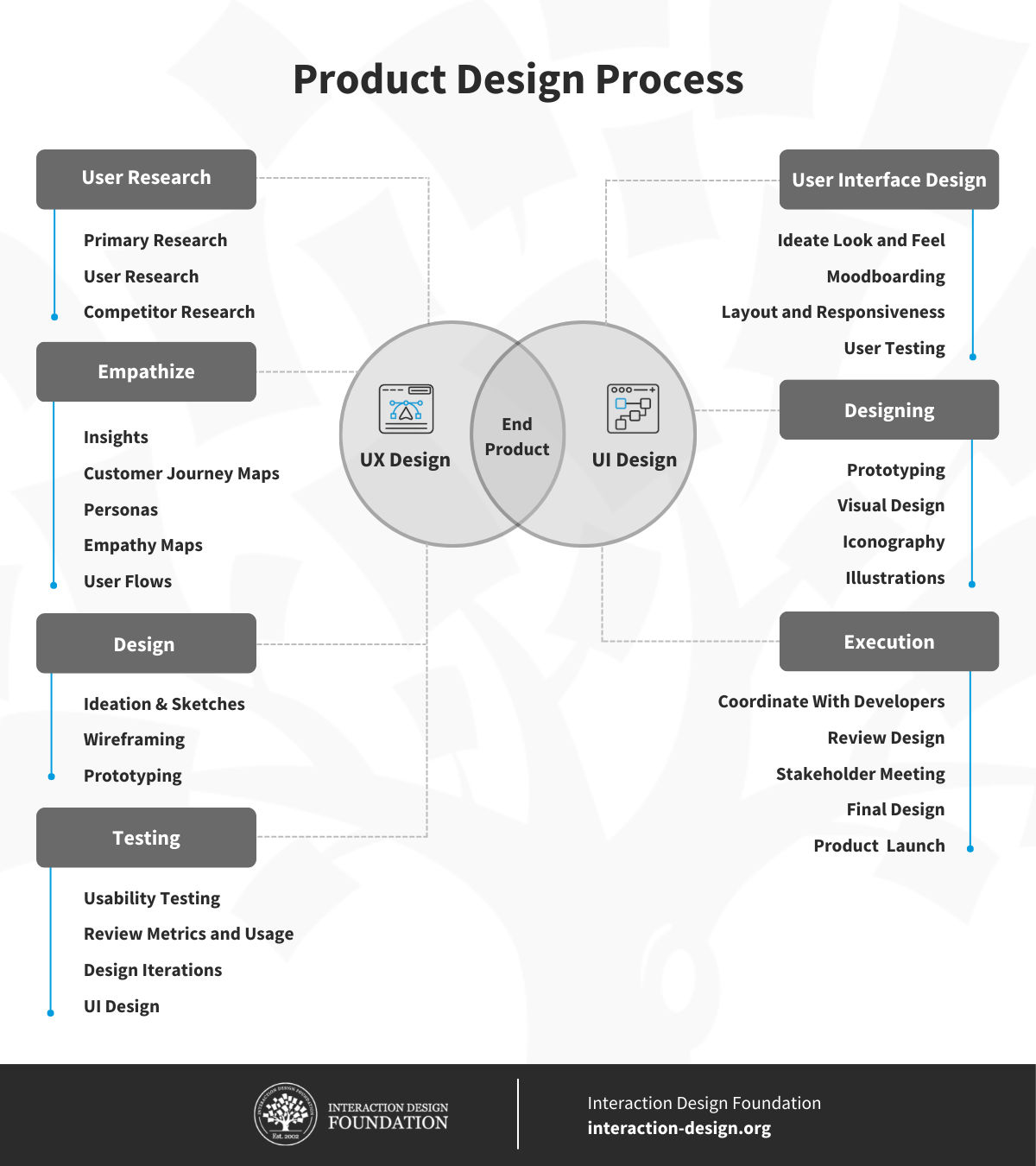
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Then, from that, they ideate and sketch design concepts based on insights they’ve gained from research. They can then move on to develop and test prototypes (starting with low-fidelity ones and then on to mid- and high-fidelity prototypes). After that, they’ll want to collect user feedback to see what’s right and wrong with the prototypes and from there refine designs. And once the prototype works best—or maybe that should be, the best prototype works best—product designers collaborate with developers, project managers, and other team members to implement their designs. It’s about a user-centered design approach—and the mission is always to make the best user experience possible for what the brand wants.
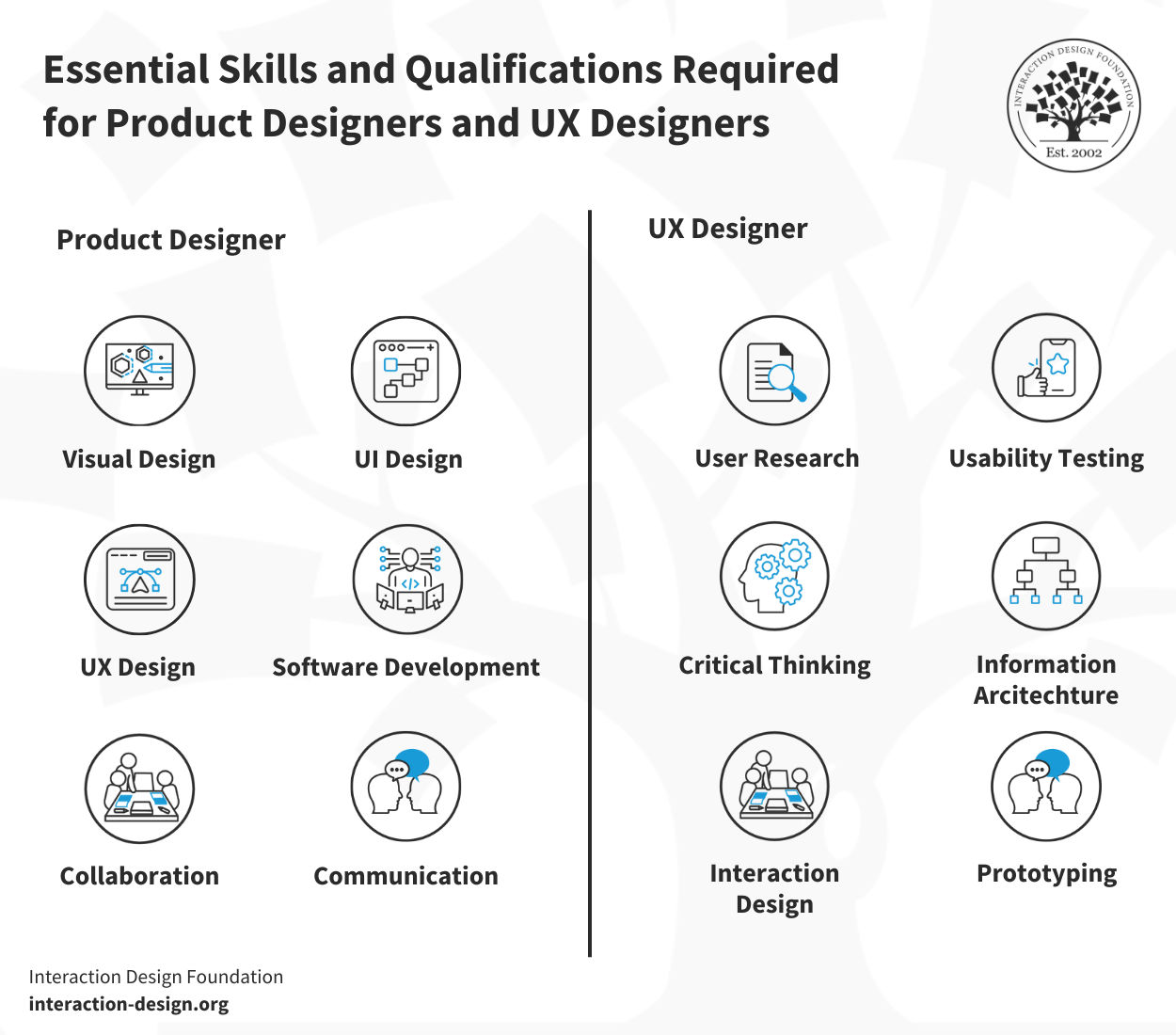
What are Key Skills and Qualifications for Product Designers to Succeed?
If you’re going to be a product designer, you’ll need a wide array of skills and qualifications to excel in the role—and the types of ones to have include:
Visual design is a big one, and it takes a good knowledge of elements of visual design—such as layout, color theory, imagery, and typography—to create aesthetically appealing products.
UI design is up there, too (not that this list is in any order as such). Skills in creating interactive visuals and front-end development contribute to designing user-friendly interfaces.
UX design is next—and it’s often confused with UI design. UX skills like prototyping, information architecture, and wireframing are things to have if you’re going to craft products that deliver a positive user experience.
Prototyping is a critical one, and the ability to quickly create prototypes that are effective is going to serve you well. Prototypes allow designers to test concepts and general approaches to understanding if the design does meet business and user goals.
User research—and effective research that includes planning, surveying methods, auditing, and all the joys of handling quantitative research and qualitative research data—is pivotal to understand user behavior and user needs.
Communication may be a so-called soft skill, but you’ll want strong communication skills to facilitate task delegation, project completion on time, and a “watertight” understanding of client requirements.
Teamwork is another one that seems to get corporate-buzzworded into overuse, but collaboration is vital in product design. It’s what nurtures the generation of solutions, understanding of project goals, and incorporation of diverse ideas.
Problem-solving completes the “trilogy” of “corporate buzzwordy” attributes, but make no mistake—you’ll want strong skills here to find innovative solutions and identify and fix design errors.
Attention to detail is in the “mix,” too, because a keen eye for detail ensures things line up with client guidelines and helps you spot areas that want—or scream for—design improvements.
Creativity is a happy ingredient—you’ll probably be glad to hear. Innovation and creativity are integral parts when you need to generate fresh product ideas and interpret stakeholder information in ways that can “wow.”
Empathy is all about the users—and rightly so, as empathy helps understand and address user needs effectively; and it’s what leads to—you guessed it—user-friendly products.
Computing awareness—in that, while you don’t need coding skills as such, a broad knowledge of what’s involved on that side of things will help you envision how the product might get realized by the developers. What’s more, you’ll be able to liaise better with development team members from having that knowledge.
(Watch this video to learn more about Empathy and why it is crucial in product design.)
Critical thinking: The ability to explore and test multiple design ideas and observe and improve design processes is more than a little valuable. You’ll need it to apply your user research in the most effective ways.
Emotional intelligence is another “biggie,” as when you’ve got a high “EQ,” you can do wonders to meet—and exceed—user needs. Think about how it can enhance user engagement and experience when you design products that bring specific emotions out of your (brand's) users.
These skills make you a proficient product designer and enhance your ability to create products that meet and exceed user needs.
What are Examples of Successful Product Designs and Their Impact?
Uber's product design shines with its Base design system—which makes functionality and visual consistency priorities. A standout feature is the one-handed design, a nifty thing that caters to on-the-go users. Key features are strategically located for easy reach for users. Flyout menus in the design enhance the experience, showcasing the profound influence of thoughtful product design.
Another compelling example is Medium. It excels in product design through its open writing platform—which makes for a nice and immersive reading and writing experience. Its minimalistic design—characterized by a clean white background—minimizes clutter and distractions. What's remarkable is its embodiment of polite design principles, carefully balancing user engagement with respect for the users’ time and attention. Notifications like subscription renewals subtly reinforce trust and respect for user choices.
What is a UX Designer?
A UX (user experience) designer focuses on enhancing user satisfaction by improving usability, accessibility, and interaction between the user and the product—and, by association, the brand behind the product. They focus on creating seamless and meaningful experiences that speak to users on all levels required for that “magic” to happen. Their work influences the entire process of acquiring and integrating the product—and that includes branding, design, usability, and function.
"There are three responses to a piece of design — yes, no, and WOW! Wow is the one to aim for."
What are Responsibilities and Job Duties of a UX Designer?
UX designers are the users’ advocates—not that product designers aren’t. “UXers” place the user at the center of the design process to ensure they meet their users’ needs and expectations in the design solution that comes out. Their responsibilities typically include the need to:
Understand and define user goals, motivations, and behaviors through user research.
Create user personas, journey maps, and wireframes to represent and guide the user experience.
Design the user interface layout and navigation flow.
Test design concepts and iterate based on user feedback and usability testing results.
Collaborate with UI designers, developers, and product managers, which will ensure the final product delivers a seamless user experience.
What are Key Skills and Qualifications for UX Designers to Succeed?
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Research is a massive one, and the ability to plan, conduct, and analyze user research is essential. It allows UX designers to understand their audience better and their needs, helping shape more effective design strategies.
Technical skills for prototyping, including familiarity with programming are up there, too. Although knowledge of actual programming in Java or JavaScript may not be required, it’s crucial to understand how live prototyping tools work.
UX design tools are vital to be familiar with—ones like Sketch and Figma—to create and adjust designs efficiently.
Information architecture (IA) is a big one, too, and organizing information in a user-friendly and intuitive way is key. This includes designing clear navigation systems, labeling, and search functions that make the product easy to use.
Wireframing skills such as creating wireframes, or blueprints, for each screen of an interface are important. They help to define the necessary elements for each page and how they will work, instead of focusing on aesthetic aspects.
Visual communication is vital, as in to be proficient in visual language. That may include an understanding of layout, color, typography, icons, images, and design theory.
Interaction design and user-centered design principles are important for UX designers, as they’ve got to understand the interaction and user-centered design principles strongly. These principles help designers create designs that facilitate a smooth user experience.
Problem-solving skills—while perhaps easy to overlook as something that “goes without saying,” excellent problem-solving skills help UX designers identify and overcome design challenges—the crux of their work.
Communication skills are another one that can be easy to overlook, but effective communication skills are vital to collaborate with various stakeholders and clearly explain design decisions.
You don’t always need a design degree to become a UX designer. Many people in this field come from different careers and have taught themselves or gone through intensive short-term programs known as boot camps.
Show
Hide
video transcript
- Transcript loading…
(Learn about the history of UX and what it means to be a UX designer.)
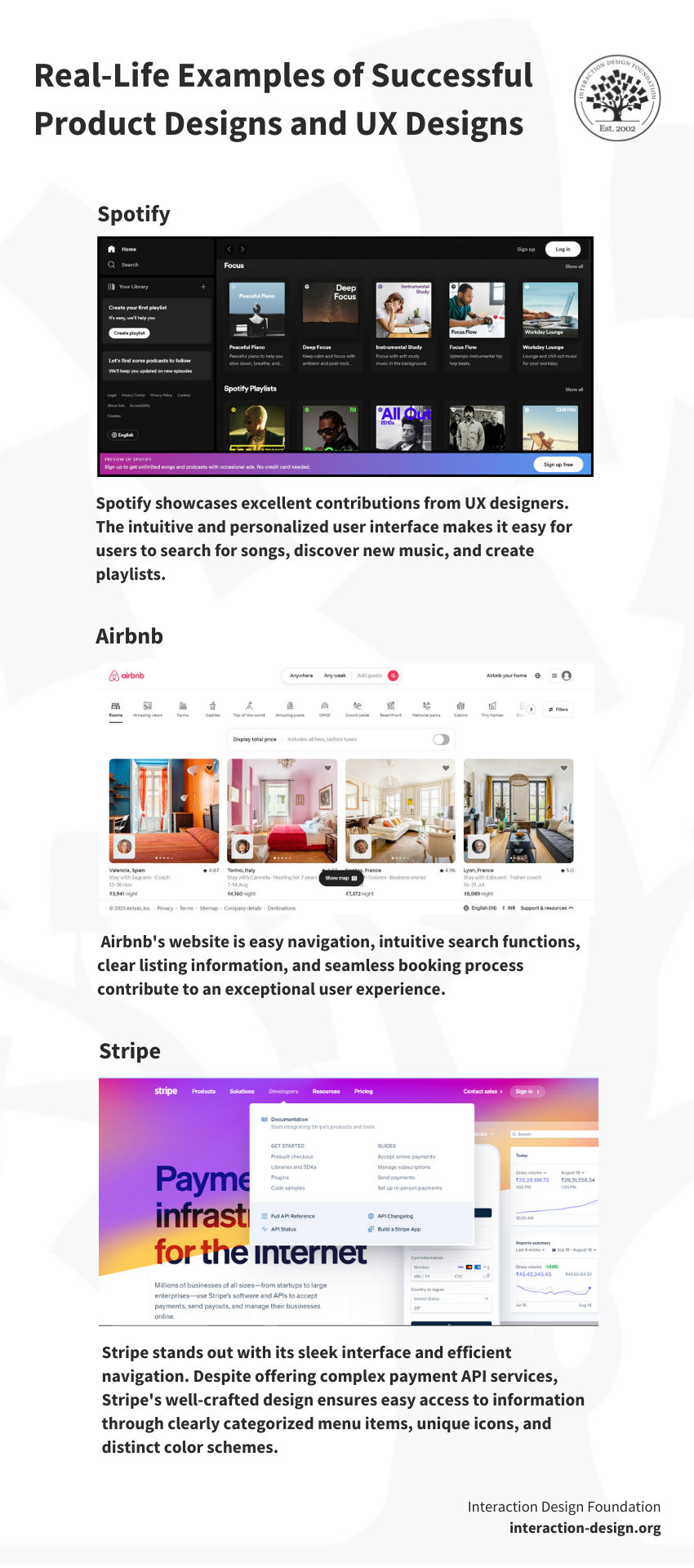
What are Examples of Exceptional UX Design in Websites or Digital Products?
We encounter countless examples of effective UX design in our digital interactions. Airbnb's website is one such example. Its easy navigation, intuitive search functions, clear listing information, and seamless booking process contribute to an exceptional user experience.
Apple's website exemplifies superior UX design with its intuitive “compare products” feature. It presents a detailed comparison of selected items in a structured, easy-to-follow format. This tool streamlines online shopping and decision-making for users—and it shows that innovation and user support can greatly elevate the digital customer experience.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
In both examples, the UX designers have excelled in understanding and meeting user needs, demonstrating UX design’s pivotal role in creating successful digital products.
What are The Differences Between Product Designers and UX Designers?
While product and UX design have a great deal in common, they’ve each got a unique focus that differentiates them. Let’s explore these roles more deeply, highlighting their similarities, differences, and exceptional contributions to the design process.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
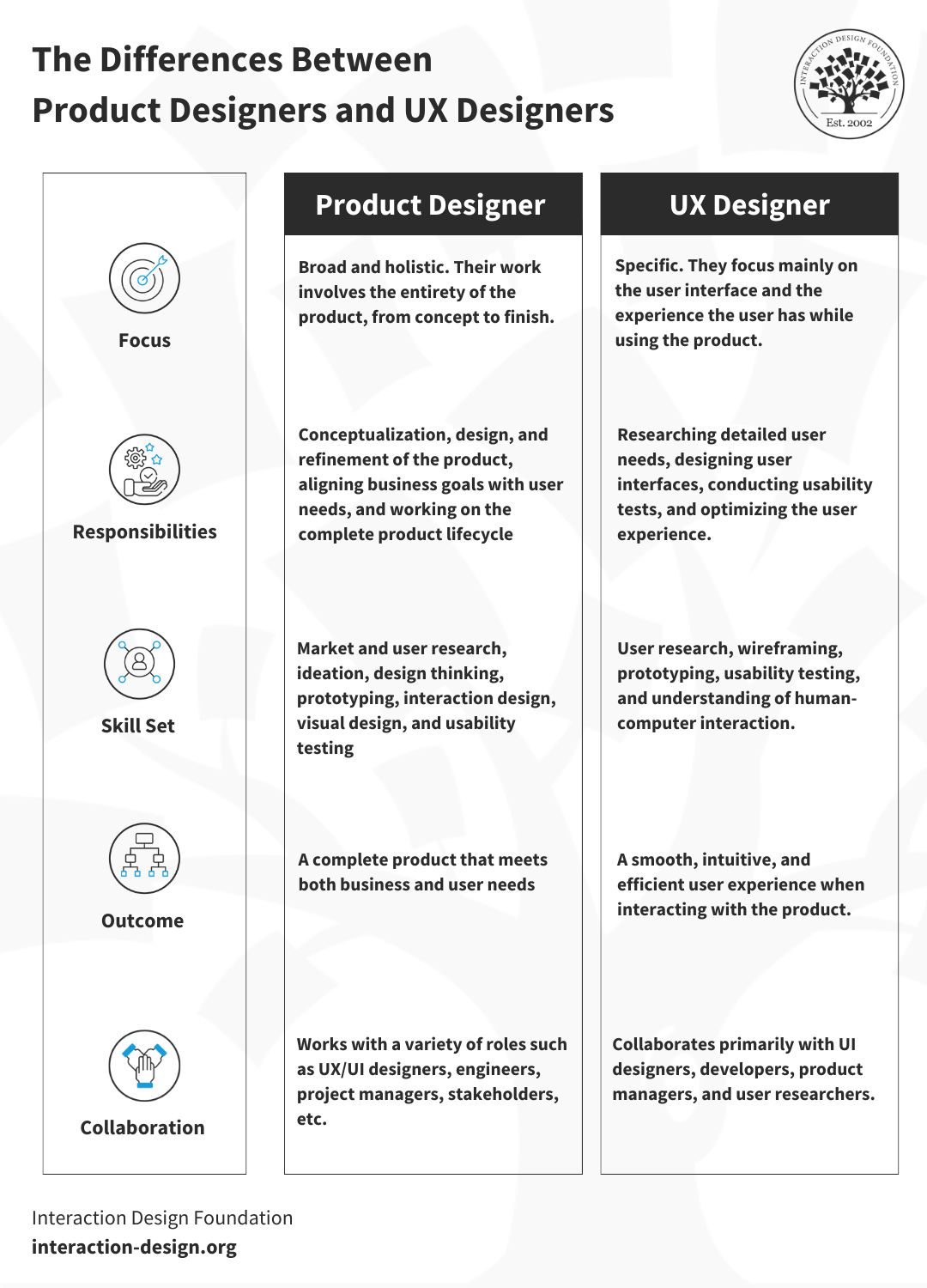
Here’s a table of differences between product designers and UX designers to give you a neat overview:
Product Designer | UX Designer | |
Focus | Broad and holistic. Their work involves the entirety of the product, from concept to finish. | Specific. They focus mainly on the user interface and the experience the user has while using the product. |
Responsibilities | Conceptualization, design, and refinement of the product, aligning business goals with user needs, and working on the complete product lifecycle | Researching detailed user needs, designing user interfaces, conducting usability tests, and optimizing the user experience |
Skill Set | Market and user research, ideation, design thinking, prototyping, interaction design, visual design, and usability testing | User research, wireframing, prototyping, usability testing, and understanding of human-computer interaction |
Outcome | A complete product that meets both business and user needs | A smooth, intuitive, and efficient user experience when interacting with the product |
Collaboration | Works with a variety of roles such as UX/UI designers, engineers, project managers, stakeholders, etc. | Collaborates primarily with UI designers, developers, product managers, and user researchers |
Product Designer Vs. UX Designer: Comparison of Job Roles
To be sure, product designers and UX designers both work towards creating user-friendly and engaging designs, but their roles differ in terms of scope and focus.
A product designer guides a product through its entire lifecycle, and that goes from initial concept to final execution. However, their responsibilities aren’t confined to user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design. They also consider business goals, market viability, and the product’s technical feasibility.
Meanwhile, a UX designer focuses primarily on the user experience. They research user behavior, create user personas, and design the interaction between the user and the product. They prioritize the user’s needs and emotions, and so they make sure the product is intuitive, satisfying, and enjoyable.
Distinct Areas of Focus and Expertise
Product design and UX design have distinct focus areas, too.
Product design: Product designers focus on the big picture. They strategize, brainstorm, and make crucial decisions about the product’s design and features. They consider various aspects of the product to deliver a complete package that fulfills the user's and the business's needs on point. These aspects may include aesthetics, functionality, and the overall business strategy.
UX design: UX designers are primarily concerned with the user’s experience. They have a deep understanding of the user’s needs, motivations, and behavior. They prototype and test designs to meet user expectations and create a seamless, enjoyable experience for all users.
Contributions to the Overall Design Process
Both roles contribute significantly to the overall design process—each in its own unique way.
A product designer tends to be involved from the initial concept to the final execution. They define the product’s direction, set design goals, and coordinate with different teams to ensure these goals are met.
A UX designer is involved from the get-go, from the very start of a project. They conduct user research, create user journeys, and test prototypes to identify and fix usability issues.
Learn more about the design process in this piece by the IxDF | Design Process
What are Real-Life Examples of Unique Contributions?
To understand the differences better, let’s consider a few examples.
Product designer: In product design, Stripe stands out with its sleek interface and efficient navigation. Despite offering complex payment API services, Stripe’s well-crafted website design ensures easy access to information through clearly categorized menu items, unique icons, and distinct color schemes. This focus on user-friendly navigation demonstrates the depth of a product designer’s role in creating a compelling, intuitive, and ultimately successful product.
UX designer: Spotify, the popular music streaming service, showcases excellent contributions from UX designers. The intuitive and personalized user interface makes it easy for users to search for songs, discover new music, and create playlists. The designers also conceived user-focused features such as Discover Weekly and Year in Review to enhance the overall experience and make Spotify a top choice for music enthusiasts.
The key in design is to know how these roles differ, and it helps put the right skills to use at the right time. Even though these roles do share some similarities, each has its own view and skills. Both of them bring a unique perspective and set of skills that contribute to creating a successful, user-friendly product.
The Interconnectedness of Roles
Despite their differences, the roles of product designers and UX designers are far from silos. In fact, there’s a significant amount of overlap and collaboration needed between the two. For example, a product designer’s decision about a feature will influence the user experience, and the UX designer’s research and testing can provide valuable insights into product development.
Skills and Qualifications
While both roles require a keen eye for design, the specific skills and qualifications differ.
Product designers: Product designers need a broad set of skills, including visual design, UI design, UX design, familiarity with software development, and an understanding of business and market strategy. They also need excellent problem-solving skills, the ability to think critically and make decisions, and strong communication skills to effectively collaborate with various stakeholders.
UX designers: UX designers need expertise in user research, usability testing, information architecture, interaction design, and prototyping. They must be empathetic to understand users’ needs, have strong problem-solving skills to improve the user experience, and be effective communicators to advocate for users’ needs.
The Impact on the End Product
Product and UX designers’ distinctive contributions greatly impact the end product.
Product designers: Product designers influence the product’s overall direction and functionality. Their decisions determine the product’s features, how it will look, and how it aligns with the company’s strategic goals and market needs.
UX designers: UX designers directly influence how users interact with the product at the same time as ensuring that business needs get met. Their work ensures the product is intuitive, enjoyable, and meets the users’ needs, influencing user satisfaction and loyalty.
While product designers and UX designers have distinct roles, they both play a critical role in creating a successful product. It’s a vital mix on a project, and using their unique skills and perspectives, they work together to create a product that meets business objectives and delivers a satisfying user experience.
Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between a career in product design or UX design will depend a great deal on your interests, skills, and the kind of work you enjoy doing. Both roles can offer rewarding and lucrative career paths. Still, each requires a different set of skills and focuses on different aspects of the design process.
1. Product Designer Vs. UX Designer: Evaluating Interests and Skills
First, you’ll want to take stock of your interests and abilities. If you love to think big-picture and enjoy handling multiple aspects of a product, this might be a sign that you’re suited for product design. What’s more, if you want to get involved in the entire product lifecycle—from conceptualization to market release—then product design could be the right choice for you. This role calls for a solid understanding of technology, user interface design, market trends, and strong problem-solving and leadership skills.
On the other hand, if you’re drawn to understanding user behavior, conducting research, and creating intuitive and engaging user interfaces, then UX design might be more suitable. UX designers often need strong empathy, analytical thinking, and skills in user research, along with proficiency in using UX design tools and creating wireframes and prototypes.
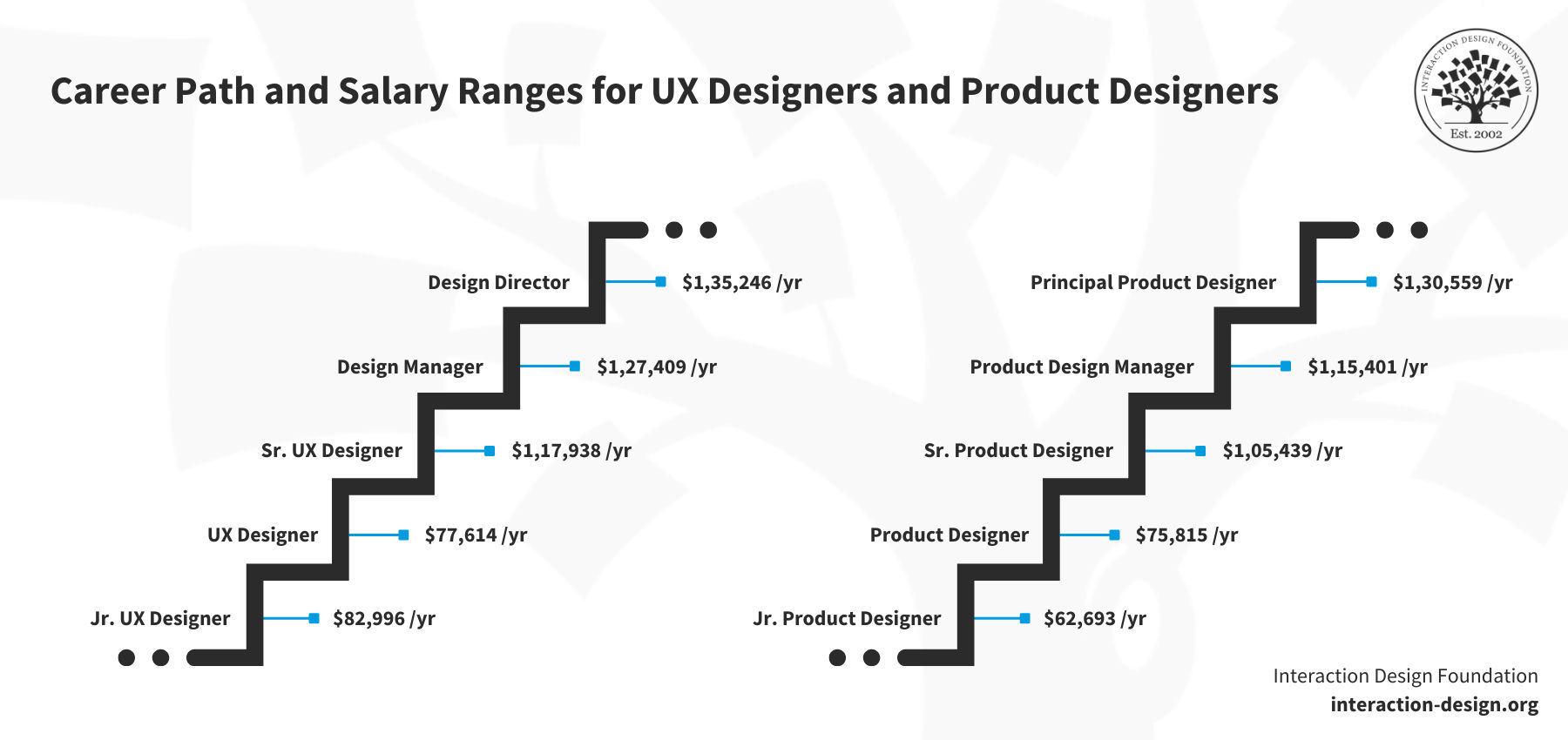
2. Product Designer Vs. UX Designer: Career Paths and Opportunities
Both fields offer significant opportunities for career growth. As a product designer, you can advance to senior roles, lead design teams, or even become a product manager. Product designers often find opportunities in tech companies, design agencies, and startups.
Product designer salary - $76,421/year
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
In the field of UX design, you can progress to senior UX designer, UX manager, or UX strategist roles. UX designers are in high demand in industries like tech, e-commerce, digital marketing agencies, and any business with a strong digital presence.
UX designer salary - $95,587/year
Learn more about the different UX roles in this piece | The Ultimate Guide to Understanding UX Roles and Which One You Should Go For
3. Product Designer Vs. UX Designer: Personal Preferences and Aptitude
Consider what you value most in a job. Product design might be the right choice if you like having varied responsibilities and directly impacting a product’s end result. However, if you prefer to specialize in creating optimal user experiences and working closely with user data and feedback, UX design could be a better fit for you.
Last, but not least, consider where your natural aptitudes lie. Do you have a knack for aesthetics, technology, and overseeing projects? You might excel in product design. But you might find your calling in UX design if you’re a strong communicator with an analytical mind and a passion for understanding and improving user experiences.
4. Product Designer Vs. UX Designer: Making an Informed Decision
Before you decide, it can be a good idea to gain some practical experience. Try taking online courses or participating in design challenges to get a feel for each role. Speak to professionals in both fields to understand their day-to-day work and their challenges to make an informed decision based on a realistic understanding of what each job entails.
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer—it’s about finding the role that aligns best with your interests, skills, and career aspirations. Whichever path you choose, both product design and UX design are exciting fields with the potential to shape the future of technology.
The Take Away
Understanding the differences between product designers and UX designers is crucial, whether you’re an aspiring designer, a hiring manager, or interested in the field. Product designers focus on the overall product, and they integrate multiple facets from concept to market. In contrast, UX designers hone in on the user experience to make products intuitive, enjoyable, and user-friendly.
Consider your interests, skills, and long-term goals when you’re choosing a career. Both fields offer rewarding career opportunities, but they each require a unique set of skills and focus. You can gain a deeper understanding of these roles to make an informed decision that aligns with your career aspirations.
Are you ready to kick-start your journey in design? Upskill for your next role with our intermediate courses, or if you're new to the field, join our beginner UX courses today! Let's embark on this exciting journey together!