Personas help you get inside your users’ heads—and build things they’ll actually value. Now imagine having a tool that makes it all click faster. That’s AI. Let it handle the grind while you do what only a human can: feel, connect, and create solutions people truly love. Here are seven ways to make your persona creation faster and smarter, plus a downloadable set of prompts and a bonus tip to take it to the next level.
AI is here to stay—and it’s changing the way we work. It can speed up workflows, take on the grunt work, and, in some situations, get us better results than we’d be able to alone. In this video, Ioana Teleanu, AI Product Design Leader (ex-Miro, ex-UiPath) and Founder of UX Goodies, explains how AI is changing the world.
Show
Hide
video transcript
- Transcript loading…
AI Can’t Create a (Good) Persona for You, But It Can Help
Want to create a user persona? It’d be tempting to open your favorite large language model (LLM), like ChatGPT, say, “Create a persona for my new product/service/experience”, and call it a day. It would certainly save you time in the short term.
The issue is that your persona would be based on generic insights from the LLM’s training data or a web search. This is almost as bad as basing your persona on assumptions—it won’t reflect your users’ specific needs and behavior patterns. In this video, William Hudson, User Experience Strategist and Founder of Syntagm Ltd, explains what happens when we don’t listen to our users.
Show
Hide
video transcript
- Transcript loading…
Another limitation is that the research process helps build deeper empathy for you and your team which guides confident decision-making. Without this, your product, service, or experience is less likely to meet user needs.
So, use AI strategically. Use it to help you with individual tasks, like producing paperwork and coding data, but don’t let it do the whole job for you. After all, AI can’t replace your deep, human-centered skills like empathy, intuition, and emotional intelligence—the skills that lead to successful products and make your career and life more fulfilling.
8 Steps to Create Personas with AI
The personas creation process involves numerous steps that vary between each designer’s approach. Here, we’ll look at an 8-step process and how AI can fit in at each stage:
Research ideation
Participant recruitment
Research planning
Transcript production
Research data coding
Affinity diagramming
Triangulation
Persona generation
At the end of this article, you’ll find a downloadable set of prompts for some of the use cases presented. And guess what? Even the prompts were created with AI’s help!
1. Research Ideation: Define Your Objectives
Research ideation is where you define what needs to be researched based on your problem and organizational goals. It transforms business challenges into clear, actionable research objectives.
LLMs can supercharge your research ideation by quickly analyzing information to identify emerging patterns and knowledge gaps. They can:
Generate diverse research questions.
Prioritize angles based on organizational goals.
Help refine problem statements.
LLMs also excel at connecting seemingly unrelated concepts, potentially revealing new research directions you might otherwise miss.
For example, imagine you're investigating why users abandon budget apps. Your preferred LLM could quickly generate targeted research questions like: "Do users leave after specific feature interactions?" and "What emotional responses occur before abandonment?" It might suggest you examine user journey friction points during days 25-35, and compare successful competitor retention strategies. This approach jumpstarts your research planning with angles you might otherwise miss.
2. Participant Recruitment: Identify Your Most Insightful Users
Your insights are only as good as your participants, so it’s crucial to find and engage the right people for your research studies. In this video, William Hudson provides the best practices to consider as you screen and recruit participants.
Show
Hide
video transcript
- Transcript loading…
AI will become your brainstorming partner as you narrow down your ideal participants and reach out to them. It can help you:
Generate targeted screening criteria based on your research objectives and existing user data.
Write personalized outreach messages that improve response rates.
Identify potential recruitment channels you might have overlooked.
Create consent forms for participants.

ChatGPT created this consent form—it is basic, but that’s often all you need. You can amend your prompt for more detailed formatting or ask for an editable document, like a .docx, to apply formatting to after.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
3. Research Planning: Write Documentation and Research Questions
Failing to plan is planning to fail.
—Benjamin Franklin
You’ve probably heard this quote a hundred times, but it still rings true. A good plan is the difference between research that drives results and research that takes you nowhere (or everywhere). AI can take on the repetitive tasks, so you can focus on squeezing as much out of your valuable research time as possible.
Research Documentation
With research comes much documentation—study plans, observer instructions, and more. This is where you will find the 10x efficiency boosts AI is known for!
Sketch out your documents in note form and get your favorite LLM to expand and tidy them up. A huge pro in this scenario is that if your results are obviously AI-produced, it doesn’t matter as long as they’re clear and understandable.
Interview Questions
How you phrase your interview questions is pivotal in how participants answer them. For example, if you ask, “Do you use a digital planner to stay productive each day?”, you assume the person uses a digital planner and links it to productivity. However, if you ask, “How do you usually plan your day?” you leave the question open to discover deeper insights that could play an important role in your productivity solution.
Draft your interview questions with the help of AI, and then have it scan and rewrite them. You might even catch bias-inducing questions you wouldn’t have, or discover a new angle to approach a topic or theme.
This approach to interview questions is used in grounded theory, a research methodology that lets user insights guide research, rather than preconceptions. In this video, William Hudson, User Experience Strategist and Founder of Syntagm Ltd, explains grounded theory.
Show
Hide
video transcript
- Transcript loading…
4. Interview Transcripts: Correct and Convert Observations for Deeper Empathy
AI is great at context. Not only can it transcribe your interviews, but it can also correct misheard sentences. However, you should always give your transcripts a once-over to ensure user insights aren’t skewed.
Once your transcripts are accurate, AI can assist you in deepening empathy. The more you and your team can empathize with your research insights and personas, the better, so you can design products your users truly love. One way to boost empathy is with the “voice of the customer”, where you rewrite your raw research in the first person. This helps you immerse yourself in your users’ world.
In this video, William Hudson explains how to write observation notes in the voice of the customer, validate them, and prepare them for affinity diagramming.
Show
Hide
video transcript
- Transcript loading…
For example, if an interview participant says, “Shopping at the end of the work day is stressful,” your AI can rewrite this as, “I don’t like to shop at the end of the day—it makes me stressed.” See the difference?
5. Code Your Research Data
If you use grounded theory for your persona research, you will code your data after each round of research. In this process, you categorize and group your data to identify areas where you need further research.
Let’s say you have hundreds of user observations, quotes, or other notes in a spreadsheet file you need to sort. Ask your LLM first to create broad categories and then narrow down later on.
Breaking this task into stages saves time, but allows you to stay in control. For example, you can ensure AI isn’t:
Creating groups that don’t align with your research goals.
Grouping by syntax instead of similarity. For example, in a transport app, grouping issues with ride availability and ride scheduling together because they both feature the word “ride”.
Once you’re happy with the broad groups and have applied your own edits, begin to narrow down, category by category. With research coded, you can ask AI for summaries of each group and subgroup. Read through these and identify where you’re missing data, or if a particular area sparks new ideas. Bounce your ideas off of AI and ask it for its own suggestions based on your problem domain and research goals.
Remember, it’s best to use AI in an assistive manner when it comes to coding. Your human insight is essential here, ensuring the nuances of your data are translated into accurate design decisions.
6. Affinity Diagrams
With a full set of research data, you’re ready for the next step. Affinity diagramming is a collaborative sense-making method where you work with key stakeholders to find patterns in data that inform your personas. In this video, William Hudson explains how to get started with affinity diagrams.
Show
Hide
video transcript
- Transcript loading…
AI can do much of the heavy lifting as you prepare for affinity diagramming. Ask AI to:
Suggest initial groupings of obviously related items as starting points (while leaving the meaningful connections to humans)
Translate participant notes if you're working with international research data.
Prepare custom instructions and reference sheets.
Once you have your affinity diagram, ask AI to highlight potential connections between seemingly unrelated clusters that you can explore further. This approach may prompt revisions to your diagram that lead you to better design choices.
7. Triangulation: Prepare Survey Questions
A best practice of persona research is to use additional research methods to validate your initial qualitative findings and the patterns you uncover in your affinity diagrams. This approach is called triangulation, and in particular, methodological triangulation. In this video, William Hudson explains triangulation.
Show
Hide
video transcript
- Transcript loading…
While you can use both qualitative and quantitative methods for triangulation, it is most common to use the latter. Surveys are a popular choice for data-driven personas, as they’re easy to distribute and gather the volume of responses you require.
AI can suggest a set of survey questions based on your qualitative research. This gives you an immediate starting point on which to build a confidence-boosting survey.
8. Persona Generation
Armed with your AI-assisted research, you can put together a persona that truly represents your targeted user group. Here’s how to get started.
Summarize Insights Ready for Your Personas
Personas should be based on a specific group of users, with similar or shared needs and behaviors that you want to delight with your product, service, or experience. Once you have identified this target audience, you can use AI to extract the condensed information you need from your research to complete your persona. You can use the template below as a guide on what to ask AI to synthesize.


Remember, personas are all about focus. This means they should be concise and not include information that doesn’t promote empathy or help you design for user needs. For example, your persona should not focus on your users’ abilities and skills, unless they are pivotal to your solution’s purpose. William Hudson explains more in this video.
Show
Hide
video transcript
- Transcript loading…
Generate Action Photos for Your Persona and Stories of Use
Photos are an essential element of a persona—they allow your team to put a face to your target user. Typically, you will use one photo—ideally an action shot—of a research participant to represent the persona. In some situations, participant photos may not be possible or unavailable. AI image generators can be far more realistic and relevant than stock images in these cases.
Your image prompt needs to be detailed and specific. If you ask for “a woman in the supermarket”, the AI will fill in the details, and you likely won’t be satisfied with the result. The image generator may also reflect inherent biases in its training data. In this example, it’s likely the image generator will give you an image of a woman with a light skin tone and who aligns with Western beauty standards. In this video, Pablo Stanley, Designer and CEO of Musho and Lummi, shows you how to structure your image prompts to be specific and avoid inherent bias.
[[video: 1948]]
Another great opportunity that AI photo generators present is to produce images of your persona in different scenarios. These images are highly beneficial to stories of use, such as user stories and storyboards, as they help foster empathy.
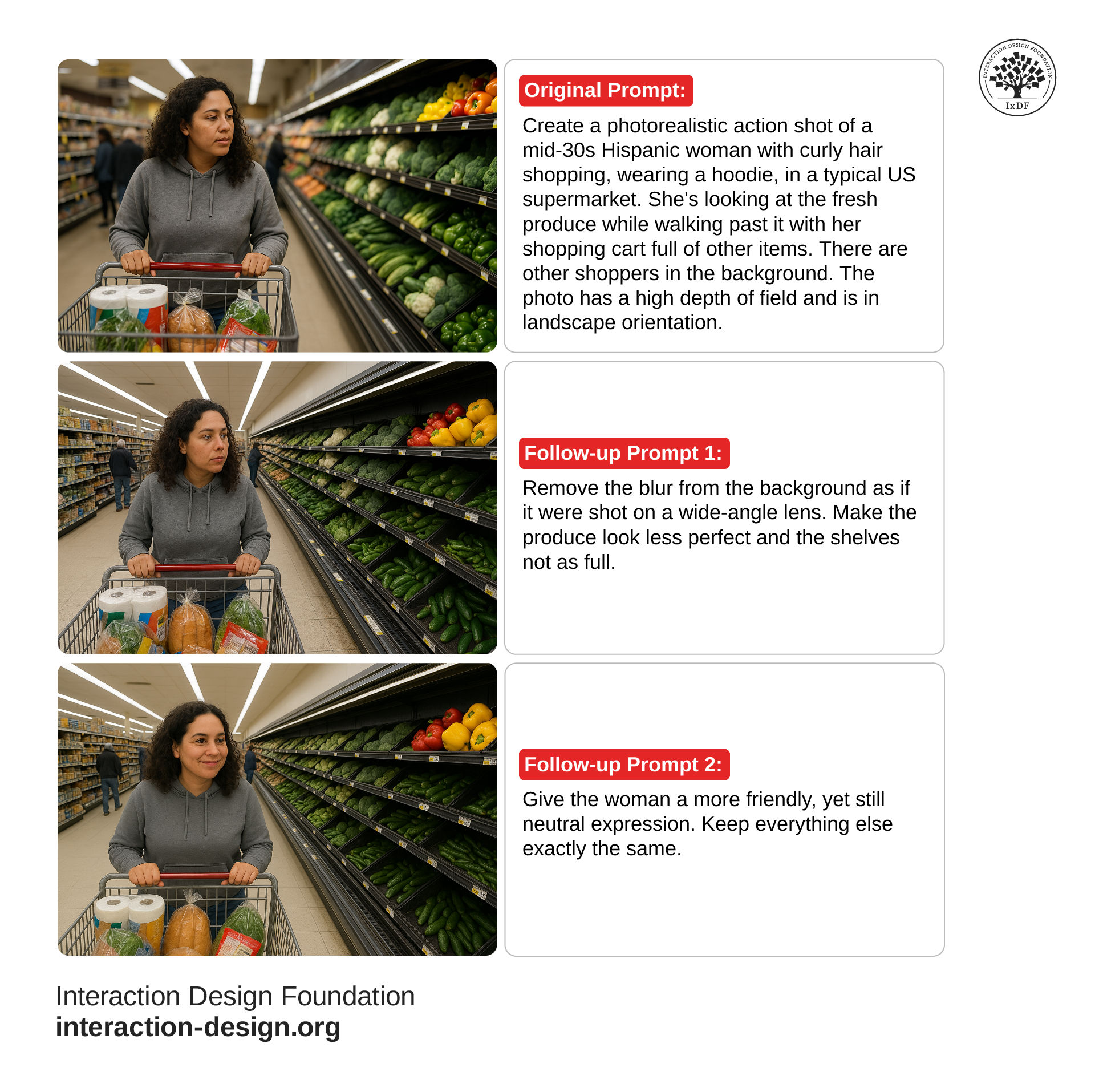
Depending on your problem domain, fine-tune your image may take a few prompts and revisions. Plus, at the time of writing, it takes image generators a few minutes to produce an image. The best method for both speed and results is still to use a real photo of a research participant, but sometimes this isn’t possible.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Download our Example Prompts
Want to get straight to results without the prompt engineering? Download our set of prompt templates based on some of the ideas in this article to get started now.
Bonus Tip: Talk to Your Research and Personas with Custom GPTs
With ChatGPT, you can create Custom GPTs. You can tailor these personalized versions of ChatGPT to specific tasks, knowledge, or communication styles. You build them using custom instructions and uploaded files—no coding required.
Here’s how you can utilize Custom GPTs with your personas.
Research Assistant
Managing vast amounts of data and insights takes time. Didn’t one participant mention preferences for store layouts? Who was that? Did anyone else talk about this? If you create an AI-powered research repository with access to all your findings, you can get answers to these questions much faster. The GPT may even make suggestions of similar data or provide some preliminary analysis for you to follow up on.
Persona Chatbot
Feed a GPT your digested persona research insights and instruct it to act as if it were a persona that came to life. You can even give it a personality and dictate how it responds. This is useful in several areas, including:
Basic Evaluations: Planning to implement a new app feature? Run it past your persona first. Do they need it? How will it solve their problems? You can use this conversation to evaluate if your idea is a good path to follow. Remember, though, personas aren’t a replacement for user interaction—use early-stage prototyping to test new features and concepts with real users.
Getting to Know You: A persona is typically represented on a page or two, either as a printout or digitally. What if, in addition to this, the persona could introduce itself to each member of your team in an individualized way? Every team member and stakeholder will get personalized responses, which can help build a deeper, more empathetic connection with your users.
Improve Your Workflow with Our Course
While AI can dramatically improve your efficiency, it can’t replace you. You’re the one with the deep, human-centered skills of empathy, intuition, and creativity that lead to products your users love. The third part of the puzzle is an easy-to-master framework where you utilize your existing skills to build personas that bring focus, align teams, and drive user-centered design.
You’ll find this framework in our course, Personas and User Research: Design Products and Services People Need and Want, along with easy templates to put into action right away, and a portfolio project that will impress recruiters. You’ll also get all the knowledge you need to convince stakeholders to get on board with personas and prove you know how to turn user insight into user love. Discover more from course instructor William Hudson in this course trailer.
Show
Hide
video transcript
- Transcript loading…
The Take Away
Meet your new user research and persona assistant, AI. With tools like LLMs and Custom GPTs, you can pour some jet fuel into your persona development process. AI can help you:
Define what to research based on the problem domain and organizational goals.
Identify ideal research participants.
Prepare briefs for researchers and participants, and other documentation.
Convert recordings into transcripts and extract insights in the “voice of the customer.”
Categorize your data during coding sessions.
Support your affinity diagram sessions and provide light analysis.
Design surveys to validate your qualitative insights.
Create personas with realistic photos and summarize goals and pain points from the research.
From here, you can move on to Custom GPTs to chat with your personas and build an interactive research repository. Always think about how you can use AI to take on repetitive tasks. The more you can safely hand off to AI, the more time you get to connect with your users and focus on building products, services, and experiences they love.
References and Where to Learn More
Want to know more about personas and how to use them effectively? Personas and User Research: Design Products and Services People Need and Want will show you how to gather meaningful user insights, avoid bias, and build research-backed personas that help you design intuitive, relevant products. You’ll walk away with practical skills and a certificate that demonstrates your expertise in user research and persona creation.
Discover how Kyle Soucy, UX Research Consultant, Trainer, and Speaker, uses AI to streamline persona and journey map creation.
Get more ideas for putting AI to use in user research with Nielsen Norman Group’s article, Accelerating Research with AI.
Take our course, AI for Designers, to see how you can level up your design process with AI.
Build out your toolkit with User Interviews’ list of 20+ AI Tools for Every Phase of UX Research You Can Use Right Now.