Rule of Thirds: The Definitive Guide & Examples
- 1.3k shares
- 1 mth ago
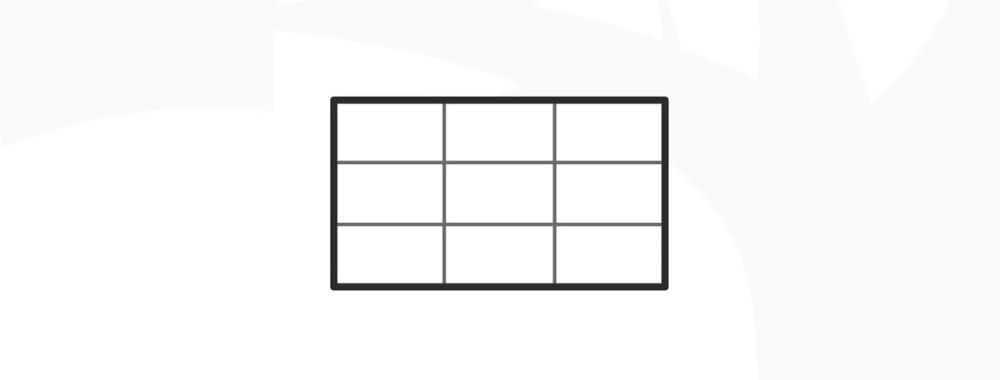
The rule of thirds is a design technique where designers divide a layout into nine equal parts through two equally spaced horizontal lines and two equally spaced vertical lines. This technique makes sures key elements—like images, text or calls to action—appear along these lines or at their intersections, and so boost user engagement and make a balanced, visually appealing interface.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
The rule of thirds has deep roots in the theory of proportions. That theory emphasizes the relationship between individual components—micro—and the overall structure—macro—in design. The rule of thirds comes from Painter and Engraver, John Thomas Smith's 1797 insights in Remarks on Rural Scenery, and it’s evolved to become a cornerstone of design alongside the golden ratio and the rule of proportions.
Designers, photographers and others who work in the visual arts have applied the rule of thirds design principle in works that are both captivating and effective—to create a sense of harmony, intrigue and more. These compositions feature strategically placed elements along the grid lines or their intersections—or the “sweet spots”—to whet visual interest and create balance. For example, the rule of thirds in graphic design is a staple technique of visual communication, one that can access viewers in a storytelling manner—or arouse their interest in other compelling ways.
The rule of thirds is a design staple that speaks volumes through the compositions it frames.
Unsurprisingly, the rule of thirds is an essential visual design technique that features greatly in UX (user experience) design. Designers particularly value it as a way to help optimize the user experience in digital products such as web pages. When designers work on user interfaces (UIs), they use the rule of thirds to guide the eyes of their target audience naturally to the most crucial parts of a site or mobile app. They can therefore improve usability and aesthetic appeal as they help users establish a sense of order, intrigue and trust in their design works.
When designers get the rule of thirds working in their designs, they align key interface elements—such as navigation bars, call-to-action buttons and key information—along these strategic points. Here are the main benefits of the rule of thirds in UI design:
Designers use the rule of thirds to establish a clear visual hierarchy in their web design work and elsewhere. This arrangement helps them highlight the most crucial elements there, like call-to-action buttons or key information. It makes them easily accessible and noticeable for users.
The rule of thirds helps make a balanced composition, too. When designers distribute elements evenly across the grid, they can stop themselves from overcrowding a design—and make sure that each component receives adequate space to “breathe.” This technique enhances how clear and readable the interface is overall. What’s more, when designers apply the rule of thirds across websites they design, it can give a really consistent and professional look to their work.
When designers put elements strategically around a screen with the rule of thirds, it doesn’t just capture user attention. It guides users’ interactions across the interface, too. This guidance is something that can greatly improve both the navigation and usability. And it can lead to better user engagement—as well as potentially higher conversion rates. For example, if designers place a primary call-to-action at an intersection point within the grid, it can draw users’ eyes towards it—and naturally so. So, users will be much more likely to interact with the call-to-action.
The rule of thirds can really help improve the user experience whenever users encounter static elements like information architecture on a webpage. Still, it also applies to dynamic elements in interactive designs, where user focus is absolutely critical.
© lovish verma, Fair Use
Another great advantage of the rule of thirds lies in its flexibility and effectiveness across different screen sizes and orientations. This adaptability is something that’s crucial in responsive design—where user interfaces have to function seamlessly across a range of devices from desktops to smartphones. With the rule of thirds, designers can create layouts that keep a high level of visual appeal and functionality, whatever the device. This makes sure users can have a consistent user experience—everywhere.
The rule of thirds also encourages designers to experiment with asymmetry so they can make layouts that are more dynamic and visually interesting. For instance, designers can place an image near two-thirds of one side rather than center it. That way, they can break the monotony of a symmetrical design. This adds an element of surprise and visual interest, and the technique’s particularly effective to draw the user's eye to specific areas of the screen. It gives a boost to both the design's aesthetic quality and its functional efficiency, too.
Amazon structures its homepage around a grid that’s divided into nine equal parts—leveraging the rule of thirds to make the best visual flow and user engagement.
© Angela Fabunan, Fair Use
UI designers use the rule of thirds in website design to organize and position elements effectively, and here's how they do it:
Designers put key elements like logos, navigation menus and call-to-action buttons at the intersection points—or along the lines. This makes for a layout that’s more balanced and visually engaging.
Designers often place images, text blocks and other content in a way that goes in line with the rule of thirds grid. They draw users’ attention to the important content and make a natural flow for their eyes to go with.
When designers align important content or interactive elements with the intersecting points or lines, they can establish a visual hierarchy that’s clear—and guide the user's focus to specific areas of the website.
Breitling watch’s design balances many elements well on one screen.
© Camren Browne, Fair Use
Designers use the rule of thirds to make sure there’s an optimal distribution of negative space or white space. This can boost the readability—and overall user experience—of the design.
When designers create content for different screen sizes, the rule of thirds helps them keep a balanced composition and adapt the layout effectively across various devices.
CEO of Experience Dynamics, Frank Spillers explains responsive design:
For more sophisticated applications, designers might choose to use variations like focusing on just the columns or rows of the grid. This can help them put emphasis on specific aspects of the content more strongly.
Nike utilizes the rule of thirds by making sure that these focal points really grab the viewer's attention.
© Angela Fabunan, Fair Use
To design rule of thirds compositions well, designers can follow these steps:
Designers should set up a basic grid on their design canvas—one that divides the space into nine equal sections. That grid will serve as the foundation for them to strategically place the design elements. It’s important to make sure that the grid lines are even in spacing both horizontally and vertically so they create a balanced layout.
Designers should focus on positioning important elements—like logos, navigation menus, call-to-action buttons and key content—at the intersections of these grid lines. These points typically attract the most viewer attention, and they can give a great boost to the design’s visual impact. The top-left intersection—for example—gets the highest visual attention at over 40%. That makes it an ideal spot for the most important information or interactive elements to go.
Designers should distribute elements across the grid to keep a visual balance. Avoid overcrowding any one part of the grid, especially the intersections. The rule of thirds encourages not just the placement of elements at the intersections but along the lines themselves, too. That can help them achieve a well-proportioned and aesthetically pleasing design.
This design’s main focus—on the crystal rocks and the beaded bracelet with an elephant—is on the left and right thirds sections, and that makes sure the visitor focuses on the center text itself: "It's not just a movement, it's a lifestyle."
© Caroline Forsey, Fair Use
When designers work images or graphical elements into their designs, they should line the subject or focal point up with the grid intersections or along the lines. This technique is crucial not just in UI/UX design but in photography, too, where the rule of thirds is a foundational skill. For example, in a landscape photo, to run the horizon line along the top or bottom horizontal grid line—and not the center—can make for a more captivating composition.
The best way to master the rule of thirds is to keep at it with continuous practice—and experimentation. Designers should apply this rule in different projects and see how it changes their design’s visual appeal as well as user interaction. They should use tools like cropping and re-aligning in post-production so they refine how they put elements according to the rule of thirds. What’s more, this can help them train their designer’s eye to naturally recognize these balance points in future projects.
Designers can make sure how effective their rule-of-thirds web designs and other visual designs are when they do their user testing well. Regular feedback mechanisms—like A/B testing and heatmaps—can further refine how they apply the rule of thirds. These can help designers understand how users interact with their creations—and where they may need to make adjustments. When designers regularly revisit these principles and adapt them based on specific project needs and user feedback, it can lead to more refined and successful design outcomes.
UX Strategist and Consultant, William Hudson explains A/B testing in this video:
Designers can choose from numerous tools to implement the rule of thirds, including the following:
Design software like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator or Sketch often include grid systems that allow designers to overlay a rule of thirds grid on their designs. This helps designers align and position elements according to the rule.
Many design softwares offer plugins and extensions specifically for grid systems and composition, such as "GuideGuide" for Photoshop and "Grid Guide" for Sketch, which enable designers to create and align designs based on the rule of thirds.
Online grid generators such as "Gridulator" and "Gridpak" let designers generate custom grid systems, including the rule of thirds—and download them to use in their design projects.
Physical grid paper and printable templates with the rule of thirds grid are ideal for sketching and initial wireframing before designers move on to digital design software.
There are mobile apps specifically for applying the rule of thirds to photographs that smartphone users take. These apps overlay the grid on the camera viewfinder, helping photographers align their shots according to the rule.
Photoshop features a handy way to apply the rule of thirds: click "View" → "Show" → "Grid".
The rule of thirds is certainly a fundamental design principle in UX and UI design. Still, it’s crucial to be aware of potential limitations and risks that may affect just how effective a design ends up being. When designers understand these considerations, it can help them make decisions that are more informed—and potentially avoid common pitfalls.
To rely too heavily on the rule of thirds may accidentally get in the way of a designer’s creativity. It might lead to designs that lack a unique feel and a personal touch. This overreliance can end up making interfaces feel standardized, monotonous—and uninspiring. Users will be less likely to take to experiences that don’t have the engaging effects they’re after.
The rule of thirds mightn’t always be the best choice for every design scenario. For instance, minimalistic interfaces—which thrive on simplicity and ample white space—or data-heavy interfaces—which call for a different approach to information hierarchy and layout—mightn’t benefit from strictly sticking to this rule.
Designers might feel tempted to put too many elements at the intersections of the grid—in the belief that doing so will capture users’ attention better. However, this can lead to a cluttered and overwhelming interface—one where the user finds it difficult to focus or find important information.
If designers use the rule of thirds incorrectly, it can result in compositions that are unbalanced and visually confusing. If designers fail to thoughtfully align elements—or if they misuse the grid—the overall aesthetic and functional quality of the design may suffer and harm the user experience.
Indeed, it’s important to create designs that are very visually appealing. Even so, designers who overemphasize aesthetics at the cost of usability can end up making interfaces that are utterly beautiful—yet hard to navigate and understand. This misalignment often results in users who are frustrated and who may not engage deeply with the product.
The rigidity of the rule of thirds can sometimes work against its application across various screen sizes and resolutions. Designs that look perfect on a desktop might not translate well to smaller mobile screens. This can lead to issues in visual coherence and user interaction.
If designers stick too strictly to the rule of thirds, they might make designs that don’t adequately consider the content they should display. This can make for a disconnect between what the design emphasizes and the actual information or functionality that needs to come across to users—which can potentially mislead users.
Designs that focus too heavily on aligning elements strictly according to the rule of thirds might overlook important accessibility considerations—like readable text sizes and easily clickable buttons. This oversight can make the interface less accessible to users with disabilities—and that’s a great risk in user-centered design.
This video explains why accessibility is such a vital concern in design:
Designers should note that to break away from the rule of thirds can work well, too. It might lead to unique and captivating designs. Depending on the project's requirements and creative direction, designers might deviate and arrive at fresh perspectives and innovative solutions—solutions that really stand out in the digital landscape.
Overall, the rule of thirds is a time-tested tool that can help improve user experience—and boost engagement and conversion. It can cast compelling imagery and build trust with a brand, too. As with other design principles, it’s important to apply it mindfully and create good-looking designs that users find useful, helpful and more.
Take our Visual Design: The Ultimate Guide course.
Read our piece, The Rule of Thirds: Know your layout sweet spots.
Read our piece, Rule of Thirds: The Definitive Guide & Examples.
Go to How to Use the Rule of Thirds in Web Design [Quick Tip] by Caroline Forsey for more helpful insights.
Discover more details at Designing a landing page with the UX rule of thirds by Angela Fabunan.
Visit What is the Rule of Thirds in Design? A Complete Guide by Camren Browne for further insights.
Find more in-depth information in How is the rule of thirds used in design? by Nate Kadlac.
The rule of thirds is a fundamental composition principle in design and photography. It improves visual balance and interaction in a layout. When designers divide the image into a grid—of three horizontal and three vertical segments—they put important elements along these lines or at their intersections. This technique encourages a more natural movement of the eye through the artwork. What’s more, it gives its aesthetic appeal a boost and makes the composition more dynamic and balanced.
Take our Visual Design: The Ultimate Guide course.
The rule of thirds and the golden ratio both guide the arrangement of elements in a design—but they do it in different ways. The rule of thirds divides the design space into nine equal parts with two horizontal and two vertical lines. To stick key elements at the intersections or along these lines creates balance and directs the viewer's eye.
The golden ratio, though, involves a more complex mathematical relationship of 1:1.618. It suggests a division of space that’s asymmetrical yet naturally pleasing to the eye. When designers use the golden ratio, they often make a focal point that runs in line with this ratio. That leads to a sense of aesthetic harmony, one that feels organic.
Although both principles aim to enhance visual interest and harmony, many professionals see the golden ratio as being more flexible. That’s due to its adaptability to different scales and its prevalence in nature. The rule of thirds is a kind of simplification of the golden ratio. It makes it easier to apply—but sometimes less dynamic.
Designers can choose between these principles based on their specific goals and the project’s context. Both methods help structure content in a way that's visually appealing and easy to navigate.
Watch as UX Strategist and Consultant, William Hudson explains the golden ratio:
Take our UI Design Patterns for Successful Software course.
Yes, cultural variations affect it. This composition principle is widely applicable, indeed, but its implementation can differ based on cultural perceptions—of space, balance and aesthetics. In Western cultures, for instance, designers often use the rule of thirds to create dynamic visual interest in a picture. They position key elements off-center to guide the viewer’s eye in a specific narrative direction.
In many Asian cultures, though, there’s a preference for compositions that are more central and symmetric. This reflects principles of balance and harmony—that are prevalent in artistic traditions like Japanese Zen gardens and Chinese landscape paintings. Here, designers might still use the rule of thirds but do it in a way that emphasizes balance and tranquility rather than dynamic movement.
These cultural preferences can influence everything from graphic design to web layouts. And it’s crucial to understand these differences for designers who work in global contexts. When they recognize and adapt to cultural variations in visual composition, designers can communicate more effectively with diverse audiences.
Watch Author and Human-Computer Interaction Expert, Alan Dix explain why it’s important to design with culture in mind:
Copyright holder: Tommi Vainikainen _ Appearance time: 2:56 - 3:03 Copyright license and terms: Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Copyright holder: Maik Meid _ Appearance time: 2:56 - 3:03 Copyright license and terms: CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons _ Link: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Norge_93.jpg
Copyright holder: Paju _ Appearance time: 2:56 - 3:03 Copyright license and terms: CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons _ Link: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kaivokselan_kaivokset_kyltti.jpg
Copyright holder: Tiia Monto _ Appearance time: 2:56 - 3:03 Copyright license and terms: CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons _ Link: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Turku_-_harbour_sign.jpg
Take our Visual Design: The Ultimate Guide course.
Yes, several tools help with this. These tools often integrate into graphic design software and applications—making it easier to align and put elements in place according to this compositional rule.
One common feature is the grid overlay. Most photo editing and graphic design programs, such as Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator, offer a grid option that you can overlay on your canvas. This grid splits the image into nine equal parts, which matches the rule of thirds layout. Designers can place key elements at the intersections or along the lines to enhance visual interest and balance.
What’s more, many camera apps on smartphones and digital cameras come with an option to show the rule of thirds grid on the screen while capturing photos. This helps photographers frame their shots according to this principle—even before they edit the images.
Some website and UI design tools also incorporate grid systems that adapt the rule of thirds. These tools help designers maintain alignment and proportion across different screen sizes, and ensure that the layout remains effective and aesthetically pleasing.
Take our Master Class Accessible and Inclusive Design Patterns with Vitaly Friedman, Senior UX Consultant, European Parliament, and Creative Lead, Smashing Magazine.
Take our Visual Design: The Ultimate Guide course.
Yes, you can. For instance, when you use the rule of thirds to position key elements in a design, you can also apply the principle of balance to make sure that these elements distribute visual weight evenly. This keeps the design from feeling too heavy on one side or the other. Alignment comes into play when you use the grid lines of the rule of thirds to line up text and other elements neatly. This can enhance the clarity and cohesiveness of the design.
Contrast can work in tandem with the rule of thirds, too. You place contrasting elements at the grid intersections or along the lines. This doesn’t just capture attention—it makes the composition more dynamic and engaging, too.
Also, the principle of movement—where you arrange elements to lead the viewer's eye across the design—is something that can benefit from the strategic placement through the rule of thirds. This creates a natural flow, and one that guides the viewer through the design in a deliberate way.
Take our Master Class Accessible and Inclusive Design Patterns with Vitaly Friedman, Senior UX Consultant, European Parliament, and Creative Lead, Smashing Magazine.
Take our Visual Design: The Ultimate Guide course.
Focus on several key aspects: viewer engagement, composition balance and the overall aesthetic appeal.
First, assess viewer engagement. Track how users interact with the design. In digital designs, tools like heat maps can show where viewers spend the most time looking. If these areas align with the intersections of the rule of thirds, it suggests that the rule’s guiding viewer attention well.
Next, evaluate the composition’s balance. A well-applied rule of thirds should create a visual balance that feels neither too cluttered on one side nor too empty on the other. This balance contributes to a more pleasant viewing experience—one which you can subjectively assess by collecting feedback from users or other designers.
Last—but not least—think about the overall aesthetic appeal. This involves looking at how well the elements within the design harmonize and contribute to a unified look. You can conduct surveys or A/B testing to see which designs viewers prefer. A design that applies the rule of thirds well is one that will often receive more positive reactions, indicating how aesthetically effective it is.
Take our Master Class How to Get Started with Usability Testing with Cory Lebson, Principal and Owner of Lebsontech LLC.
Take our Conducting Usability Testing course.
Here are some common ones. One typical error is over-reliance on the grid. While the rule of thirds does give a helpful guide, to rigidly put every element along the grid lines or intersections can make a design feel forced or unnatural. It's important to use the grid as a guideline rather than a strict rule—permitting some flexibility to achieve the best visual outcome.
Another mistake is to ignore the context of the elements within the design. For instance, if a key element like a call-to-action button or a focal image aligns perfectly with a grid intersection but clashes with other important components or text, the overall composition might suffer. Designers must consider the interplay between all elements, and ensure they complement rather than compete with each other.
Finally, some designers forget to consider the viewer's natural reading patterns. Those patterns vary from culture to culture. For example, in Western cultures, people typically scan images and text from left to right. It can boost the readability—as well as engagement—to place the most significant elements in a design accordingly. Not thinking about these patterns can lead to a disconnect with the audience.
Watch Author and Human-Computer Interaction Expert, Alan Dix explain why it’s important to design with culture in mind:
Copyright holder: Tommi Vainikainen _ Appearance time: 2:56 - 3:03 Copyright license and terms: Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Copyright holder: Maik Meid _ Appearance time: 2:56 - 3:03 Copyright license and terms: CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons _ Link: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Norge_93.jpg
Copyright holder: Paju _ Appearance time: 2:56 - 3:03 Copyright license and terms: CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons _ Link: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kaivokselan_kaivokset_kyltti.jpg
Copyright holder: Tiia Monto _ Appearance time: 2:56 - 3:03 Copyright license and terms: CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons _ Link: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Turku_-_harbour_sign.jpg
Take our Visual Design: The Ultimate Guide course.
Yes, the rule of thirds applies to mobile app design. It serves as a powerful tool to create interfaces that are both visually appealing and functional. This rule helps designers put important elements—like buttons, logos and navigation items—in places that are easy to access and notice. When designers divide the screen into nine equal parts with two horizontal and two vertical lines, they can find strategic spots for these key components.
To apply the rule of thirds in mobile app design boosts the user experience by making sure that crucial information and interactive elements get the attention they deserve. For example, to position a call-to-action button at one of the intersections can make it more prominent—and encourage users to click. Similarly, to get text or important content aligned along these lines can improve the readability and make the information more digestible.
What’s more, this compositional rule helps maintain visual balance in the app’s layout—something that's especially important given the limited space on mobile screens. By distributing elements thoughtfully across the grid, the design avoids overcrowding and creates a cleaner, more organized interface.
CEO of Experience Dynamics, Frank Spillers explains UI patterns and how to use them:
Take our Mobile UI Design course.
Koliska, M. (2021). Guided by the Grid: Raising Attention with the Rule of Thirds. Journalism Practice, 15(4), 524-541.
This publication has been influential because it gives a comprehensive analysis of the rule of thirds. Despite the widespread use of this rule, there’s little research to understand how professionals apply it in practice. This study examines the use of the rule of thirds in photographic composition—and draws on a survey of 181 participants who evaluated 590 window views. The authors used a tree-regression model to predict view satisfaction based on the application of the rule of thirds. The findings suggest that the rule of thirds can be a useful tool to create images that are visually engaging, as it helps to draw the viewer's attention to key elements within the frame. This research contributes to a better understanding of the cognitive and perceptual processes involved in visual composition—and it has implications for fields such as photography, graphic design and visual communication.
Samara, T. (2023). Making and Breaking the Grid, Third Edition: A Graphic Design Layout Workshop. Rockport Publishers.
This book’s been influential in the field of graphic design because it gives a comprehensive and accessible guide to understanding and applying the rule of thirds. The updated third edition of this classic text includes a cross-cultural and inclusive re-envisioning of design history related to the grid—as well as expanded discussions of grid use in interactive and UX/UI scenarios. The book is filled with hundreds of large, full-color layout concepts and diagrams that educate and inspire designers. It doesn’t just teach the basics of the grid system—it shows how to effectively break the rules to create unique and visually engaging layouts, too. This book is an essential resource for designers who work in any medium, as it helps them develop a deeper understanding of the cognitive and perceptual processes that are involved in visual composition.
Remember, the more you learn about design, the more you make yourself valuable.
Improve your UX / UI Design skills and grow your career! Join IxDF now!
You earned your gift with a perfect score! Let us send it to you.
We've emailed your gift to name@email.com.
Improve your UX / UI Design skills and grow your career! Join IxDF now!
Here's the entire UX literature on The Rule of Thirds by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Take a deep dive into Rule of Thirds with our course Visual Design: The Ultimate Guide .
Master complex skills effortlessly with proven best practices and toolkits directly from the world's top design experts. Meet your experts for this course:
Mia Cinelli: Associate Professor of Art Studio and Digital Design at the University of Kentucky.
Joann Eckstut: Color Consultant, Founder of The Roomworks, and one of the 12 designers chosen by the Color Association of the USA to create the yearly forecast used by industries to keep up with color trends.
Arielle Eckstut: Author, Agent-at-large at the Levine Greenberg Rostan Literary Agency, and Co-Founder of The Book Doctors and LittleMissMatched.


We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge. Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change, , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge!
