UX case studies form the core content of a UX professional’s portfolio. They are essential to getting you hired, because case studies are a window to your professional practice, by showing how you think, adapt, cooperate and ultimately solve challenges. A UX case study has to tell a story about you. Like all good stories, case studies benefit greatly from a solid structure that guides the reader through your thinking and experience. Here, we will explore how to craft the perfect structure for your UX case studies.
Let’s begin with a few quotes about case studies and interviews, from UX recruiters worldwide, compiled in 2017 by Cassandra Naji (marketing content manager at Justinmind, the popular UX prototyping software):
”I want to see how you think strategically, how you connected the dots to land at the right solution. What does your process look like? What steps did you take to learn more about your users?” (Melissa Perri, Product Manager and UX Designer at Produx Labs)
”Having a really strong portfolio where you can talk through your whole process, not just showing research, user flows, wireframes, etc, but turning it into a story for example why you moved onto each part of the process so a hiring manager can really get inside your thought process.” (Tom Cotterill, UX Recruiter at Source LF)
”Storytelling is important. The interviewer wants to understand your process, your contribution to the team, and how your mind works.” (Rebecca Levi, UX/UI/Product Design Recruiting Manager, The Joanne Weaver Group)
“My tip would be, tell stories. When designers present a flat portfolio it doesn’t tell me about how they approach the work they do and how they deal with the ebbs and flows of design. Tell me how you navigate from start to end of a project, I like to see a case study approach.” (Sarah Bellrichard, SVP of Wholesale Internet Solutions & UX at Wells Fargo)
“So, when I interview you, tell me a story about how you made something awesome even though it was super uncertain what it was going to turn out to be. And get meta and walk me through how you approach problems, how you navigate through idea generation and synthesis, and how you build solutions.” (Jeff Onken, Design Strategist & UX Manager at Northrop Grumman)
You might begin to see the pattern here: Recruiters from both large and small companies alike are all immensely interested in the same thing: your thinking and professional process. They want you to tell them a story about how you tackled previous UX challenges. To progress through to an actual interview, where you can elaborate on your stories in person, first you must pass the portfolio review obstacle – UX case studies in your portfolio are your first opportunity to tell recruiters your stories. These stories have to be tantalizing enough that the recruiter will want to invite you to learn more about them, and you. So, in order to get the recruiters’ attention, first we need to understand the power of stories, so we can understand why they are so much in demand by recruiters, and then see what story elements your UX case study should contain.
The power of storytelling in UX hiring
In our long history as a species, stories have always played an important role in our societies. Pick any time and any populated place on the planet, and some research into that culture during that era will bear this out as a fact. Writer and copyeditor Shannon Turlington (2010) offers some excellent insight from her 20+ years of experience in science and academic writing, about the importance of stories for humans.
“We use stories not only to learn but also to speculate, to pose questions and then find solutions.”
- Shannon Turlington
Through storytelling, we pass on important information and lessons from generation to generation. Some stories are fictional; others are accounts of true events. But we don’t use stories just to learn. Stories are also an exercise in speculation and the exploration of possibilities. They are a great way to ask the “what if” questions in life, and find possible answers to these. In fact, storyboarding is one of the most well-known UX tools used to do just that!
Since we don’t know how the stories of our own lives will end, absorbing stories that have a beginning, middle and end can provide great satisfaction. Generally speaking, stories have the ability to provoke strong emotional responses, so they are an immensely powerful tool that can connect people to one another and, if sufficiently persuasive, bring about dramatic and profound changes in thinking.

Copyright holder: Gerd Leonhard, Flickr. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-SA 2.0
For UX professionals, telling the story of how they tackled the challenges of wicked UX design problems provides recruiters with the confidence that an applicant has great communication skills, matched with excellent technical skills and a deep understanding of methodological approaches to product development.
Assuming that you might be looking for a UX job in the near future, let’s take a look at who is going to be hiring you. They have a specific and immediate need in mind: to find a new member to join their UX team, someone brilliant who will bring inspiration, talent and hard work that will raise the team to new heights. We already know from their testimonials above that they are interested in your stories. Why?
Quite simply, by going through applicants’ portfolios, recruiters are subconsciously asking themselves a what-if question: “What if this person joined our team? What would it be like to work with this person?”. Therefore, what better way for you to answer this question for them than to provide a story? Telling a great story about your own experiences as a UX professional gives this satisfaction of having something come full circle: starting from somewhere and arriving somewhere else. It helps the recruiter see the world through your own eyes, and in the process, hopefully recognize someone who has fought a difficult challenge with skill, integrity, commitment, courage and perseverance – just the right kind of person to solve the wicked problems of design.
Structuring a captivating story
Orson Scott Card, an American science-fiction writer, wrote in 2010 that most novels are dominated by four types of story structures: milieu, idea, character and event. From this classification, we can single out the “idea” structure because it accurately frames the type of experience that a UX professional has throughout his or her working life. In Card’s own words:
“Idea stories are about the process of seeking and discovering new information through the eyes of characters who are driven to make the discoveries. The structure is very simple: The idea story begins by raising a question; it ends when the question is answered.”
– Orson Scott Card
Idea stories have a structure of discovery, so the question is naturally a “why”, “how” or “what if”, exactly the type of thing that UX professionals ask themselves daily. So, in this context, there is a question that begets an answer (that’s the design problem), the protagonist (i.e., you as a UX professional) tells the story of how he or she arrived at an answer for that question (helping the reviewer see the process through the protagonist’s eyes), and, finally, there is a conclusion, an answer to the question (that’s your final product and its impact).

Copyright holder: Smita Nair Jain, Flickr. Copyright terms and license: Public Domain
A good UX case study is the story of how you broke a design challenge down into its components, and then expertly put this knowledge together to deliver a superb user experience.
Turning a UX case study into a story
Of course, we’re not saying here that you need to write a whole novel to explain what happened in a UX project you undertook in the past. A case study has to be succinct, but all the crucial elements of the story need to be there: the starting question, the process, the answer. And remember that just like any project that you designed, your UX case study is also a product of design – something that you give shape and essence to, with care and attention to detail, attempting to solve a real need: the recruiter’s need to see how you think, and, through this, your own need to become employed. So, we can conclude that the perfect UX case study has three parts, which we will outline next.
The beginning of a UX case study
Here is where you should explain the question that you tried to answer, and the context. For example, look at how the following statement describes the goals, vision and challenges to be addressed by a project:
“We wanted to design a new app that reminds busy people to do important things. The challenge was that simple reminders are often issued at a place or time where the user can’t really act on them, like a reminder to buy milk, while the user is at the office. Wouldn’t it be better to issue that reminder as the user is walking past a supermarket, on the way home?”
If you were part of a larger UX team here, you should also state your role in the project – for example, you might write something like “My role in the project was to undertake user research and evaluation of prototypes”.
The process of the UX case study
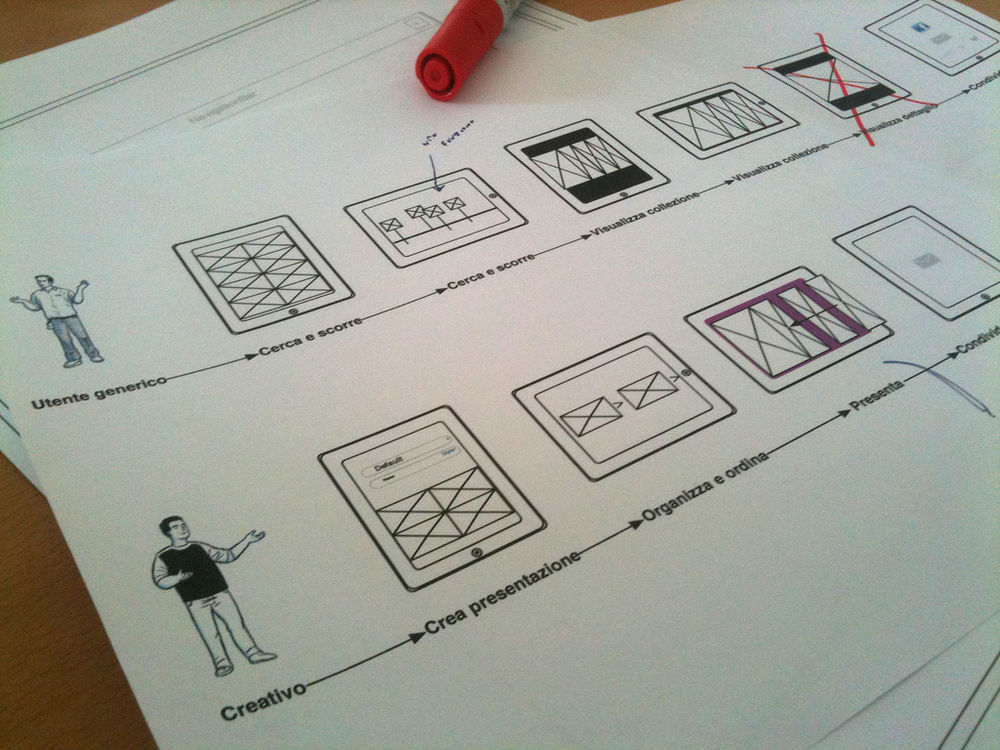
This part of the case study explains the steps that you took to arrive at a solution. Here, you should highlight the activities that you took and illustrate those activities with sketches, photographs, diagrams or other design artifacts or deliverables that you produced. Bear in mind that the focus here is on the process, so emphasis on iterations, rising challenges, alternatives, decision points and conflict resolution is paramount.
You should always start with some user research that frames the problem. For example, you might write this:
“We analyzed the to-do lists of 140 users aged 18-40 for a period of 3 weeks and discovered that about 60% of their tasks were location-dependent. From this analysis, we made 4 user personas and defined their experiences in managing to-do lists with customer journey maps.”
You could show one persona and one journey map here to illustrate.
Then, show how you progressed into ideation for solutions – for example, putting in a sequence of sketches that shows a user interface design evolution from napkin drawing, to low-fidelity wireframes, then interactive low-fidelity prototypes and a final pixel-perfect design shows that you have progressed from early concepts to an end product.
It’s important to annotate these with information, too, which describes how the evolution took place through consultation and evaluation. For example, next to your napkin drawing, you might say “we carried out a focus group with 20 users to co-design an early prototype based on this idea” and then show 2-3 alternative low-fidelity UI sketches that emerged as an output of that process. Then you might show a wireframe emerge from these sketches and say something like “undertaking heuristic and lab-based user evaluation, we selected Alternative 2 as the way forward, but improved it with features from Alternatives 1 & 3 which were found to work better in the lab”.
The conclusion of the UX case study
This last part of the structure shows your final answer to the original question. It’s not enough here simply to show your final deliverable. In this section, you have to demonstrate impact – how did your designed product improve the situation? Remember that the final step in every Design-Thinking process is evaluation. So, mention what you learned through lab tests, field tests, analytics mining or other data you have – e.g., “In a 3-week field trial with 30 users, we found that these location-sensitive reminders led to less cluttered to-do lists for our users, since they were able to act on the reminders and cross them off their list instead of postponing them.” Charts and statistics are great for demonstrating this impact.
However, don’t just stay stuck on the impact bit. It’s also important to highlight the lessons you learned and that you later reflected on your experience. What would you do differently if you had more time or resources to spend on the project? You might say this, for example: “We found that 20% of the tasks in the to-do lists related to things that other people had to do, instead of the user. We didn’t have the budget or time to address this challenge, but in the future, we could revisit the project and focus on collaborative aspects of task management.” Do remember to acknowledge your co-workers and collaborating stakeholders in the last section, too, as this shows a teamworking spirit.
“To design is to communicate clearly by whatever means you can control or master.”
— Milton Glaser, celebrated American graphic designer
UX case studies are an exercise in communication
One of the most important skills for a UX professional is the ability to communicate. A UX case study is a demonstration of that ability, so writing good case studies doesn’t only demonstrate your technical and other professional skills; it also gives you a chance to prove how effective your communication skills are.
We will end this piece with a final note on UX case study structures. Many UX professionals believe that a great case study should end with a great product, but this is not always the case. First of all, remember that greatness is a relative attribute – what works well for you might be less than optimal for the person next to you and his/her own circumstances. It is also a temporary attribute: An app that was great back in 2005 was probably next to useless by 2017 – given that so much of the hardware and people’s lives had changed in the interim. However, what remains is the process – how you masterfully employed your critical thinking and knowledge of methodology to solve a difficult design problem, in the context and constraints that applied to the project at the time.
In this sense, don’t be shy to demonstrate those grand projects where the shining element was your approach to the work, even though the end product might have lost some of its luster.
The Take Away
A UX case study is an account of the events that led you to the discovery of some new knowledge, the answer to a UX design problem. Keeping in mind the recruiters’ need to answer their “what if” question (i.e., “What would it be like if this person joined our team and we had to work with him/her every day?”), structuring your case studies in the shape of an “idea” type of story will help recruiters get a glimpse of the world through your eyes, and provide a (hopefully) positive response to their question.
Your case study is a glimpse into your way of thinking: It is a demonstrator of process and critical reflection, rather than of the end product. There are only three parts to a UX case study structure (the beginning, the process and the conclusion), but knowing how much and what type of content is appropriate for each part will get you off to a good start on writing eye-grabbing case studies.
References & Where to Learn More
Hero Image: Copyright holder: Jacopo Romei, Flickr. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-SA 2.0
Course: “User Experience: The Beginner’s Guide”
Turlington, S. (2010). Why are stories so important?
Card, O. S. (2015). The 4 Story Structures that Dominate Novels
Naji, C. (2017). 8 tips for UX job interviews: questions & insights from UX managers