How to Supercharge Your Design Workflow with AI
- 590 shares
- 2 mths ago
Prompt engineering is the process of creating effective prompts for artificial intelligence (AI) systems. A prompt in AI is a specific instruction or input given to an AI system to elicit a desired response or output. Effective prompt engineering results in good communication between the user and the AI system, where the user guides the AI systems to generate the desired outputs.
To craft effective AI prompts, designers need to understand the capabilities and limitations of the AI model. For instance, a well-engineered prompt can lead to more accurate and nuanced responses from an AI like ChatGPT.
In this video, AI product designer Ioana Teleanu explains how you can communicate and interact with AI effectively.
Prompt engineering is crucial to harness the power of AI tools for a design process; the quality of a designer’s prompts will determine how well they can collaborate with AI tools and thus, elevate their design projects.
Prompting and Prompt Engineering are closely related concepts in AI, but they serve slightly different functions:
Prompting is the act of providing an AI system with an initial input or instruction. In design, prompting involves the creation of specific directives or creative briefs to guide the AI's output. For example, a designer might prompt an AI tool to generate logo designs by providing details like brand values, color preferences, and thematic elements.
Prompt Engineering is a more advanced and nuanced practice. It involves crafting prompts to optimize the AI's performance and output quality. It's not telling the AI what to do, but doing it in a manner that leverages its capabilities and algorithms most effectively. For instance, a prompt engineer would experiment with different phrasing, structures, or contextual elements in the prompt to get the best possible design output from the AI.
Prompting is about giving directions, and prompt engineering is about fine-tuning those directions to harness the full potential of the AI. Designers use prompting to communicate their basic requirements, whereas prompt engineers delve deeper into the mechanics of how these requirements are communicated to achieve the most desirable and efficient outcomes.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Prompt engineering is vital to ensure effective, accurate, and ethical interactions with AI. It’s also a central part of human AI interaction. Prompt engineering allows:
Effective Communication with AI: Prompts are the primary mode of communication between humans and AI models. A well-engineered prompt effectively conveys the user's intent and leads to more accurate and relevant responses from the AI.
Reduce Misinterpretations: AI models can sometimes misinterpret vague or poorly structured prompts. This leads to irrelevant or incorrect responses. Effective prompt engineering minimizes misunderstandings and enhances the reliability of AI interactions.
Ethical AI Use: Proper prompt engineering can help to align AI responses with ethical guidelines and cultural sensitivities. This is crucial to prevent the propagation of biases, misinformation, or harmful content.
Facilitation of Human-like Interactions: Good prompts can make AI interactions more conversational and human-like.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
AI prompts can have the following input formats:
These are the most common and involve written instructions or queries to the AI. Text prompts are versatile and can be used for a wide range of tasks, from the generation of written content, like articles and reports, to more specific design-related tasks, such as website copy or product descriptions.
Image prompts are visual inputs to guide the AI. This could include providing an existing image to inspire a new design or asking the AI to analyze and interpret visual data. In design, image prompts are particularly useful for tasks like image editing, graphic design, and pattern generation.
Audio prompts include sound clips or voice instructions. They are essential in tasks like voice recognition, sound design, and music composition. In UX design, audio prompts can help develop voice-user interfaces.
Video prompts involve the use of video clips to instruct or guide the AI. These can be used for video editing, the generation of video content, or the analysis of video for research and design purposes, such as user behavior analysis.
These prompts involve real-time interaction, often used in AI systems that respond to user inputs, like chatbots or interactive design tools. They are crucial to develop interfaces that require user engagement and feedback.
These prompts blend multiple types of content, such as text with images or audio with video, to provide a more comprehensive instruction set to the AI. This is particularly relevant in complex design tasks that require a multi-faceted approach, such as multimedia content or integrated marketing campaigns.
Each type of prompt has its specific applications and can be used to guide AI in different aspects of design and creative work. The choice of prompt depends on the task at hand and the capabilities of the AI system being used.
There are several types of prompts, each with distinct characteristics and applications:
One-Shot Prompts: These are single instructions given to an AI model to generate a response or perform a task without prior examples. They are straightforward and concise.
Example: "Design a logo for a bakery."
Zero-Shot Prompts: These prompts require the AI to perform a task without any previous training specific to that task. They rely on the AI's pre-existing knowledge.
Example: "Predict the main design trends for 2024."
Few-Shot Prompts: These include a few examples to guide the AI. This approach helps the AI understand the context or format of the desired output better.
Example: "Given these three examples of minimalist website designs, create a similar layout for an online store."
Chain-of-Thought Prompts: These prompts guide the AI through a reasoning process or a series of steps. They are helpful for complex tasks that require logical progression.
Example: "First, list the essential features of a user-friendly mobile app interface, then design a prototype based on these features."
Instructional Prompts: These are detailed, step-by-step instructions for the AI to follow. They are particularly useful for tasks that require specific actions or sequences.
Example: "Create a step-by-step plan to conduct user experience research for a new app."
Iterative Prompts: Involve refining or evolving the AI's output through a series of prompts based on feedback or changes in requirements.
Example: "Start with a basic layout for a web page, then iteratively add elements based on user feedback."
Each type of prompt serves a different purpose, from quick and straightforward tasks to complex, multi-step processes.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
In design, various types of prompts prove useful, each to different aspects of the design process:
Exploratory Prompts: These prompts encourage brainstorming and ideation.
Example: "Propose five innovative packaging designs for eco-friendly products, emphasizing sustainability."
Refinement Prompts: They aim to improve and refine existing designs.
Example: "Enhance the user interface of our mobile app to improve navigation and accessibility for users over 50."
Constraint-Based Prompts: These prompts include specific limitations or requirements.
Example: "Create a poster using only two colors and geometric shapes to convey a message about digital privacy."
Target Audience Prompts: These prompts are tailored to specific user demographics or personas.
Example: "Design a website layout for a children's educational platform, making it engaging and easy to navigate for ages 6-10."
Scenario-Based Prompts: They involve the creation of designs for specific situations or use cases.
Example: "Develop an emergency evacuation map for a large shopping mall and ensure clarity and ease of understanding under stress."
Trend-Informed Prompts: These prompts incorporate current design trends.
Example: "Incorporate minimalist aesthetics and bold typography in the branding materials for a new fashion label."
Problem-Solving Prompts: They aim to address specific design challenges.
Example: "Redesign the checkout process of our e-commerce site to reduce cart abandonment rates."
Innovation Prompts: They encourage thinking outside the box.
Example: "Imagine a futuristic smart home interface, integrating AI and IoT in a user-friendly way."
In this video, AI product designer Ioana Teleanu shares practical tips to create effective text prompts.
Designers can follow these guidelines to write effective prompts:
Be Specific and Clear: Clearly define the task's objectives, requirements, and constraints. Specificity helps AI understand precisely what you're looking for.
Provide Context: Explain the background and the broader project goals. Context helps AI to align its output with the overall vision.
Set Boundaries: Outline what to include and what to avoid. This helps prevent unwanted elements in the design.
Incorporate Examples: Provide examples or references. Examples guide the AI in the right direction, especially when dealing with subjective elements like style or tone.
Iterate and Refine: Use the initial output to refine the prompt. Iteration helps in honing the AI's understanding of the requirements.
Collaborate with AI: Treat AI as a tool in the design toolkit. It can provide suggestions and automate tasks, but the final creative decisions should come from the human designer.
Understand AI's Capabilities: Know what AI can and cannot do. This knowledge will help designers set realistic expectations and use AI effectively.
Experiment: Don't be afraid to try different prompts and approaches. Experimentation can lead to innovative and unexpected design solutions.
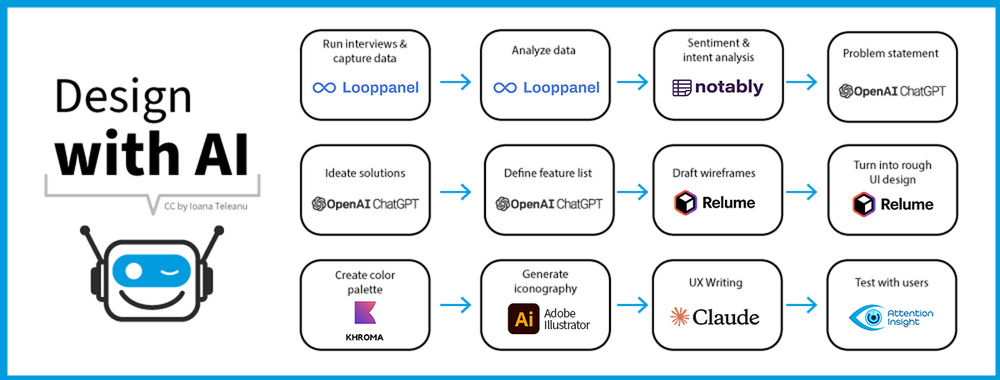
In this video, Ioana Teleanu shares how to incorporate AI into the design process.
Prompt engineering in design has several significant use cases:
Designers can automate the generation of standard design elements, like buttons or icons, freeing designers to focus on more complex aspects.
Prompt Example: "Generate a set of buttons with rounded corners, gradient backgrounds varying from blue to green, and white text, adhering to our brand guidelines."
Designers can use AI prompts to quickly explore a wide range of concepts. This is especially useful in the early stages of a project to quickly explore different directions.
Prompt Example: "Create five unique homepage layouts for a lifestyle blog, incorporating a minimalist aesthetic with interactive elements."
AI can generate designs tailored to specific user demographics or preferences based on prompts that include detailed user profiles or personas.
Prompt Example: "Design a user profile page for a fitness app that adapts to the user's age, gender, and fitness level, displaying personalized workout plans and nutrition tips."
Designers can incorporate data analytics into prompts to create designs that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also optimized for performance metrics like user engagement or conversion rates.
Prompt Example: "Using user engagement data, redesign our e-commerce product page to highlight the most clicked items and optimize for higher conversion rates."
Designers can incorporate accessibility guidelines into the AI prompts to create designs that are accessible to a broader range of users, including those with disabilities,
Prompt Example: "Produce a website layout compliant with WCAG 2.1 guidelines, featuring high contrast colors, screen reader-friendly navigation, and easy keyboard accessibility."
AI can help to create designs that adapt to user interactions or environmental changes, based on prompts that specify the desired interaction patterns or adaptive behaviors.
Prompt Example: "Develop a dynamic UI for a weather application that changes its theme and layout based on current weather conditions and user location."
Rapid prototyping of designs based on different AI-generated variations can speed up the testing process and provide quick feedback for iterative improvements.
Prompt Example: "Generate three variations of a landing page for A/B testing, each with different call-to-action placements and color schemes to evaluate user interaction patterns."
Prompt engineering, while innovative, comes with its set of challenges. One common obstacle is the generation of irrelevant or unexpected responses from AI. To counter this, designers must refine their prompts, focusing on specificity and clarity. Another hurdle is the AI's occasional inability to comprehend abstract concepts inherent in design tasks. Overcoming this requires iterative testing and learning the nuances of AI's language processing capabilities.
A crucial practice in prompt engineering is iterative refinement. Start with a broad prompt, analyze the output, and then gradually narrow down the focus. Keep a log of prompts and their corresponding outputs so that you can review it to understand patterns and make necessary adjustments.
Also, communities of practice can provide insights and shared experiences for learn more on how to craft effective prompt.
Worried AI will replace you? It won't just yet. But a designer using AI might. Take the course, AI for Designers, to master how to collaborate with AI, rather than competing against it. You’ll gain practical, future-proof skills to integrate AI into your workflow and design for AI-powered products.
Learn more about how to write text prompts in the article, How to Craft Effective Text Prompts for Design
A prompt engineer is a professional skilled in designing, optimizing, and refining prompts to effectively guide AI responses, particularly in natural language processing and machine learning contexts. Their role encompasses a thorough understanding of AI model intricacies, crafting prompts that are clear and tailored to elicit specific responses, and continuously fine-tuning these prompts for improved accuracy and relevance.
This process involves a blend of technical expertise, creative problem-solving, and iterative testing. A prompt engineer also stays abreast of the latest AI developments to innovate and solve complex challenges, playing a pivotal role in enhancing the interface between humans and AI systems for optimized communication and effectiveness.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
Prompt whispering is a technique to craft prompts to effectively communicate with AI systems, especially those based on natural language processing. It involves a deep understanding of the AI's language model, allowing for the creation of clear, context-rich instructions that guide the AI towards desired outcomes.
This process often includes refinement and iteration, tailoring prompts to leverage the AI's strengths while avoiding ambiguity. It's a skill that combines a thorough knowledge of AI capabilities with creative problem-solving, essential for achieving precise and relevant AI-generated responses, especially in tasks requiring nuanced understanding and specific outputs.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
Prompt engineering and prompt whispering, while related, differ in their focus and application within AI and machine learning.
Prompt Engineering: This is a more technical and systematic approach to crafting prompts for AI systems. It involves understanding the mechanics and algorithms of the AI model to create prompts that effectively elicit the desired response or output. Prompt engineering is about optimizing the interaction with the AI to achieve high accuracy and efficiency. In practice, prompt engineering is used to fine-tune AI systems for specific tasks, ensuring that the prompts are aligned with the AI's capabilities and limitations.
Prompt Whispering: On the other hand, prompt whispering is more of an artful and nuanced practice, focusing on the subtle and creative aspects of interacting with AI systems, especially those involving natural language processing. It involves a deep understanding of how the AI interprets language and context, and the ability to phrase prompts in a way that guides the AI towards a desired outcome, often through trial and error and iterative refinement. Prompt whispering is less about the technical optimization of the AI and more about effectively communicating with the AI to achieve specific, often creative or complex, results.
In summary, prompt engineering is a technical discipline focused on optimizing AI interactions, while prompt whispering is a more intuitive and creative practice aimed at skillfully guiding AI to achieve nuanced outcomes. Both are essential in different contexts for harnessing the full potential of AI technologies.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
Yes, ChatGPT, like other advanced AI language models, utilizes prompt engineering. Prompt engineering is integral to the design and operation of these models, ensuring that they understand and respond to user inputs effectively. Here's how it's applied:
Initial Model Training: During the training phase, AI models like ChatGPT are fed a large dataset of text prompts and corresponding responses. This training involves carefully designed prompts that help the model learn language patterns, context understanding, and appropriate responses.
User Interaction: When users interact with ChatGPT, they provide prompts in the form of questions or statements. The model uses its training and prompt engineering principles to interpret these inputs and generate relevant responses.
Response Refinement: The effectiveness of ChatGPT in understanding and responding to prompts is continually refined based on user interactions, feedback, and ongoing model adjustments.
Contextual Understanding: Prompt engineering also involves equipping ChatGPT with the ability to understand the context within a conversation, allowing it to provide more accurate and relevant responses over a sequence of exchanges.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
To start in prompt engineering, focus on building a foundation in AI and natural language processing, primarily through self-study, online courses, or formal education in related fields like computer science or linguistics. Develop proficiency in programming languages like Python and familiarize yourself with key AI models like GPT-3 and BERT. Practice writing and refining prompts, and observe how different AI models respond to variations in language and structure.
Engage with online communities for insights and feedback, and apply your skills in real or hypothetical projects to gain practical experience. Given the rapidly evolving nature of AI, staying updated on the latest developments is crucial for success in this field.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
AI prompting does not always require coding skills, especially for basic or general use. It largely depends on the level of complexity and the specific tasks you aim to accomplish with the AI. Here's a breakdown:
Basic AI Prompting: Everyday users and non-technical professionals can engage with AI using natural language inputs—no coding required. This applies to interactions with AI chatbots, search engines, or digital assistants.
Advanced AI Prompting: Customizing AI models for specific tasks, like data analysis, benefits from coding knowledge, typically in languages like Python, especially when using machine learning libraries or APIs.
Prompt Engineering: In professional settings like prompt engineering or AI research, a deeper understanding of coding, AI principles, and natural language processing is essential. Coding skills are crucial for developing, training, and managing advanced AI models.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
Designers can leverage prompt engineering in various ways to enhance their creative process and output:
Enhancing Creativity: By crafting detailed prompts, designers can guide AI to generate unique and innovative design elements, expanding their creative possibilities.
Improving Efficiency: Prompt engineering can automate repetitive tasks, allowing designers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of their projects.
Tailoring User Experiences: Designers can use prompts to create customized experiences for different user groups, enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
Exploring Multiple Concepts Quickly: Rapid concept exploration becomes feasible with prompt engineering, as AI can quickly generate a range of design alternatives based on different prompts.
Data-Driven Design Decisions: Integrating data insights into prompts allows designers to create more effective and user-centric designs.
Accessibility and Inclusivity: Prompt engineering can be used to ensure designs meet accessibility standards and cater to diverse user needs.
Testing and Iteration: Designers can use AI to quickly prototype and test different design variations, gaining valuable feedback for iterative improvements.
Cross-Disciplinary Inspiration: Prompt engineering allows for the blending of ideas from different fields, fostering cross-disciplinary innovation in design.
By effectively using prompt engineering, designers can not only streamline their workflow but also push the boundaries of traditional design practices, leading to more innovative and user-centric solutions.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
To optimize prompts for efficient AI collaboration in design, designers should:
- Understand AI Capabilities: Know the strengths and limitations of the AI to create realistic prompts.
- Be Specific and Detailed: Provide clear, detailed instructions to guide the AI towards desired design outcomes.
- Use Iterative Refinement: Refine prompts based on AI responses, honing in on the most effective language and details.
- Incorporate Design Principles: Embed key design principles into prompts to ensure aesthetically sound outputs.
- Leverage Examples and References: Use visual or textual references to guide the AI’s creative process.
- Balance Creativity and Constraints: Clearly define creative goals and practical constraints in prompts.
- Test and Learn: Experiment with different prompts to understand which yields the best results.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest in AI advancements to enhance prompt crafting skills.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
Remember, the more you learn about design, the more you make yourself valuable.
Improve your UX / UI Design skills and grow your career! Join IxDF now!
You earned your gift with a perfect score! Let us send it to you.
We've emailed your gift to name@email.com.
Improve your UX / UI Design skills and grow your career! Join IxDF now!
Here's the entire UX literature on Prompt Engineering by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Take a deep dive into Prompt Engineering with our course AI for Designers .
Master complex skills effortlessly with proven best practices and toolkits directly from the world's top design experts. Meet your expert for this course:
Ioana Teleanu: AI x Product Design Leader (ex-Miro, ex-UiPath). Founder, UX Goodies.

We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge. Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change, , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge!
