UI & UX Designer Salaries: How Much Can I Earn in 2026?

- 936 shares
- 4 days ago
AI prompts are instructions or commands given to an AI system. These prompts guide the AI to generate outputs that align with the user's intentions.
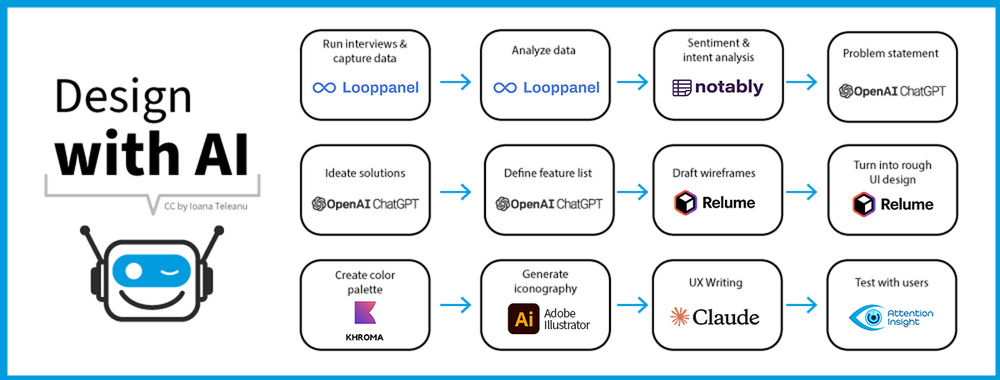
In this video, AI product designer Ioana Teleanu explains how designers can effectively communicate and interact with AI.
In design, AI prompts can be textual descriptions, visual cues, or coded instructions that direct the AI to produce specific design elements, styles, or concepts. For instance, a prompt could be as straightforward as "design a minimalist logo for a coffee shop" or as complex as "generate a 3D model of an eco-friendly urban space." The versatility and adaptability of AI prompts make them invaluable tools in a designer's toolkit.
Effective prompts are essential to use AI systems successfully. Designers use prompts to communicate with AI software like ChatGPT or Midjourney. The quality of the input—the prompt—will determine the quality of the output.
At the heart of AI's functionality lies machine learning. In machine learning, AI algorithms learn from vast amounts of data, identify patterns and make decisions based on that data.
The quality and nature of the data fed into these algorithms significantly impact their performance and accuracy. This is where AI prompts come in—they guide the learning process and provide context and direction to the AI. For instance, when training an AI to generate web designs, the prompts might include various styles, layouts, and user interface elements, teaching the AI the nuances of good design.
Once trained, AI systems can turn raw inputs to high-quality outputs.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
The role of AI prompts in machine learning extends beyond mere instruction; they help to shape the AI's understanding of design principles and aesthetics. A well-designed AI prompt can lead to an AI that not only understands the technical aspects of design but also grasps the subtleties of artistic expression and style.
Some of the most relevant AI prompts for designers are textual and visual prompts.
Textual prompts are written descriptions or commands used in AI applications like content generation, chatbots, or design tools. For example, a designer might use a textual prompt to instruct an AI to create a website layout that is "clean, modern, and user-friendly."
AI tools such as Midjourney can translate text inputs such as "Draw me an image of a mountain at sunset" to produce a visual output.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Visual prompts, on the other hand, involve providing images or visual elements to guide the AI to generate similar styles or patterns. This is particularly useful in graphic design and visual arts, where AI can create artwork or design elements based on a given image or color scheme. For example, you might upload a sketch of a wireframe (the visual input) and ask the AI to generate a high-fidelity UI.
The effectiveness of an AI prompt largely depends on its clarity, specificity, and alignment with the AI's capabilities. A well-crafted prompt not only directs the AI toward the desired outcome but also opens up possibilities for creative exploration. It's a delicate balance between giving enough direction to produce relevant results and leaving enough ambiguity for the AI to introduce innovative and unexpected solutions.
AI prompts can be categorized based on complexity, particularly their interaction with AI models. Here are the main types:
One-Shot Prompts: These are single, standalone prompts that require the AI to respond or take action based on that single input alone. They are straightforward and do not rely on previous interactions or context.
Example: Asking an AI a single, isolated question like "What is the tallest mountain in the world?" The AI responds with a straightforward answer, "Mount Everest," without needing any additional context.
Contextual or Follow-Up Prompts: These prompts build on previous interactions. The AI must consider the context or history of the conversation to provide a relevant response.
Example: After discussing historical landmarks, ask, "Which of these is located in Italy?" The AI recognizes the context from the previous conversation about landmarks to identify landmarks in Italy.
Chain-of-Thought Prompts: These require the AI to follow a sequence of thoughts or logical steps to arrive at an answer. It's more complex as the AI must demonstrate a process of reasoning.
Example: "If a train travels at 60 mph for 2 hours, and stops at 3 stations for 5 minutes each, how far does it go? Provide all the reasoning steps to explain the answer." The AI must demonstrate the calculation process, showing that it understands the steps to solve the problem.
Creative or Generative Prompts: Such prompts task the AI with generating original content, like stories, artwork, or music. These prompts often require more creativity and interpretation from the AI.
Example: "Write a poem about a peaceful forest in autumn." The AI generates an original poem, capturing the essence of autumn and the tranquility of a forest.
Interactive or Dynamic Prompts: These prompts involve a back-and-forth interaction where the AI's responses can change based on real-time input or feedback from the user.
Example: In a design tool, "Adjust the color scheme of this layout to be more vibrant and engaging." The AI makes real-time adjustments based on the prompt and can further modify the design based on ongoing feedback.
Complex Task-Oriented Prompts: These prompts are used in specific professional or technical contexts, requiring the AI to perform complex tasks, often involving data analysis, problem-solving, or decision-making.
Example: "Analyze the sales data from the last quarter and identify emerging market trends." The AI processes the data, identifies patterns, and provides insights into market trends based on the analysis.
Designers need to balance precision and creativity to craft effective AI prompts. To successfully communicate with an AI system, prompts must be clear and detailed yet open-ended enough to allow for creative exploration. First of all, designers need to understand the capabilities and limitations of the AI and tailor the prompts to it. For example, the same prompt will lead to different results in ChatGPT than in Midjourney.
Moreover, vague or overly broad prompts can lead to unpredictable or irrelevant outputs. For instance, a prompt like "design a logo" is too open-ended and could result in many outputs. A more effective prompt would be "design a minimalist logo for a vegan bakery using green and brown colors," which provides specific direction and style cues.
Designers must also experiment with AI prompts and continually refine them prompts based on the AI's outputs to get closer to the desired outcome. This process is not just about the right design but also about understanding how different types of prompts influence the AI's outputs.
In this video, AI Product Designer Ioana Teleanu shares practical tips to create effective text prompts.
In design, AI systems open up new avenues for creativity, efficiency and innovation. In graphic design, for instance, designers use AI prompts to guide the AI to generate logos, layouts, and visual elements, significantly speeding up the design process and offering many creative options. In UX/UI design, designers use AI prompts to create the desired user interfaces, test usability, and even predict user behavior, which results in a better overall user experience.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
One of the most exciting aspects of AI in design is its ability to generate entirely new concepts and ideas. Designers can use specific prompts to explore styles and aesthetics that they might not have considered and push the boundaries of traditional design thinking. For example, the prompt "futuristic, biomimetic architectural design" could lead the AI to produce models and visualizations that blend organic forms with advanced technology, which might be challenging and time-consuming to conceive manually.
AI makes design tools more accessible to non-designers. This means that individuals or small businesses without extensive technical design expertise can still produce high-quality designs with the help of AI-driven design platforms. AI can empower users to create professional-level designs as these tools become more intuitive and user-friendly.
In product design, designers can use prompts to guide the AI to conceptualize and model new products. They can input the requirements and specifications into an AI system and use AI as a rapid prototyping tool. This saves time and allows for a more experimental and innovative approach to product design.
As with any technological advancement, the integration of AI in the design process raises several ethical considerations. The primary concern is the potential for bias in AI-generated designs.
AI systems learn from datasets; if these datasets contain biases, the AI will likely replicate them in its outputs. To minimize this risk, designers must be vigilant and curate the data and prompts they feed into AI systems. Designers should craft prompts that ensure diversity and inclusivity in these datasets to produce fair and unbiased designs.
Another ethical consideration is originality and intellectual property. AI-generated designs are based on existing data and patterns, which raises concerns about the authenticity of the designs and the potential for inadvertently copying existing works. Designers must navigate these concerns carefully and ensure that AI-generated designs are genuinely innovative and do not infringe on existing copyrights.
The increasing reliance on AI also raises concerns about the devaluation of human creativity and skills. As AI becomes more capable, there is a fear that human designers might become obsolete or that the value of human-generated designs might diminish. It's crucial to view AI as a tool to enhance human creativity, not replace it. The designer's role is evolving to include AI as a collaborator, which requires a new set of skills to guide and interpret AI outputs.
Looking to the future, AI prompts are set to become even more integrated into the design process. Advances in AI technology will lead to more sophisticated and intuitive prompt-based design tools. We can expect design tools to fully integrate AI systems that better understand and interpret human language and context. Therefore, designers might interact with design tools through natural language rather than technical skills.
One exciting prospect is the development of AI systems that can engage in a more interactive and collaborative design process. Imagine an AI that can not only generate designs based on prompts but also provide feedback, suggest improvements, and even understand and adapt to a designer's style and preferences. This level of interaction would represent a significant leap forward in AI-assisted design and offer unprecedented levels of customization and personalization.
The integration of AI in design is also likely to lead to new design aesthetics and styles that are currently unimaginable. AI's ability to process and combine vast amounts of data can result in unique and innovative design elements and push the boundaries of what is considered possible in design.
Moreover, as AI technology becomes more accessible and user-friendly, we can expect a democratization of design. Individuals and small businesses will have the tools to create high-quality designs previously only possible for professional designers. This could lead to a more diverse and vibrant design landscape, with a broader range of voices and perspectives represented.
In the near future, AI prompts are expected to evolve in several key ways:
Increased complexity and nuance: As AI models become more sophisticated, they'll be able to understand and respond to more complex and nuanced prompts. This will allow for more detailed and specific instructions, leading to more accurate and tailored outputs.
Better contextual understanding: Future AI models will likely have improved abilities to understand and retain context over longer interactions. This means prompts can build upon previous interactions and allow for more conversational and dynamic exchanges.
Personalization: AI prompts will become more personalized and adapt to individual users’ styles, preferences, and needs. This could involve the AI learning from past interactions to effectively tailor its responses.
Multimodal interactions: The evolution of AI will likely incorporate more multimodal prompts, combining text, voice, images, and possibly other sensory inputs, leading to richer and more interactive AI experiences.
Ethical and responsible design: As AI becomes more integrated into daily life, the design of prompts will increasingly consider ethical implications, privacy, and responsible AI use.
Automation and assistance in prompt crafting: Tools and systems may emerge to assist to craft effective prompts and make it easier for those without technical expertise to interact with AI systems efficiently.
Overall, AI prompts are set to become more sophisticated, personalized, and context-aware.
Worried AI will replace you? It won't just yet. But a designer using AI might. Take the course, AI for Designers, to master how to collaborate with AI, rather than competing against it. You’ll gain practical, future-proof skills to integrate AI into your workflow and design for AI-powered products.
Learn more about how to write text prompts in the article, How to Craft Effective Text Prompts for Design.
Prompts are instructions or queries that guide AI systems to respond or act in specific ways. They direct the AI's responses, set the context and parameters for its operations, initiate actions or processes, and facilitate learning and adaptation.
Essentially, they are the primary means through which users communicate their needs and objectives to AI systems.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
To find good AI art prompts, focus on being specific about the subject, style, colors, and mood. Familiarize yourself with various art terms and styles for precision. Incorporate inspirational elements but leave room for creative interpretation. Experiment with different prompts and refine based on the outcomes. Keep informed about the AI tool's evolving capabilities and draw inspiration from existing AI-generated art. This approach helps craft effective prompts that guide AI to produce art aligned with your preferences.
Learn more about how to write text prompts in the article, How to Craft Effective Text Prompts for Design and take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
In ChatGPT, prompts are the user-provided inputs or instructions that direct the conversation and responses of the AI. These prompts vary widely, from straightforward questions like "What's the weather today?" to more complex requests such as "Explain the theory of relativity in simple terms." The AI uses these prompts to understand the user's intent and context, generating relevant and informative responses.
The effectiveness of ChatGPT's responses often depends on the clarity and specificity of the prompts it receives, making them a crucial aspect of the interaction between the user and the AI.
To learn more about prompts for ChatGPT, read A Prompt Pattern Catalog to Enhance Prompt Engineering with ChatGPT.
Negative prompts in ChatGPT refer to inputs that guide the AI to avoid specific topics, themes, or types of responses. They are used to steer the conversation away from undesired areas and ensure that the AI's outputs remain appropriate and aligned with specific guidelines or user preferences. For instance, a negative prompt might instruct the AI not to discuss sensitive political topics, use certain types of language, or venture into areas outside its scope of expertise.
These prompts are essential to maintain a constructive and suitable dialogue, especially in sensitive or regulated contexts.
To learn more about prompts for ChatGPT, read A Prompt Pattern Catalog to Enhance Prompt Engineering with ChatGPT.
To start a prompt, especially for AI like ChatGPT, begin with a clear and direct statement or question that specifies what you want to know or achieve. For example:
"Tell me about the history of the Roman Empire."
"Create a daily workout plan for beginners."
"Explain how solar panels work."
Start with the main idea or request, ensuring it's specific enough to guide the AI towards the desired response or action.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
AI prompts aid in design processes and help generate innovative ideas and concepts. They enable rapid production of design variations and facilitate faster and more efficient iterative processes. AI can also provide analytical feedback on designs, offering constructive suggestions for improvement.
Furthermore, these prompts can automate routine or repetitive tasks within the design workflow, freeing designers to concentrate on more creative and complex aspects of their projects.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
Yes, AI prompts can generate design ideas or concepts. When given specific instructions or themes, AI can produce creative and diverse design concepts and offer a range of possibilities that can inspire and guide designers in their work.
Learn more about how to write text prompts in the article, How to Craft Effective Text Prompts for Design and take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
Examples of AI tools that can create UI prototypes from prompts include:
Adobe XD's AI components: Adobe XD offers AI-driven features that can assist in generating design elements and layouts based on user input.
Figma's Autolayout: While not entirely AI-driven, Figma uses smart features for responsive design, which user prompts can guide to create efficient layouts.
Sketch2Code by Microsoft: This tool uses AI to convert hand-drawn sketches into HTML code, creating a basic UI prototype from a simple drawing.
Uizard: An AI-powered tool that transforms wireframes into UI prototypes, understanding user prompts and sketches to generate digital designs.
These tools demonstrate the evolving integration of AI in the UI/UX design process.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
Beginners can learn and study basic AI concepts, experiment with AI design tools like Adobe XD and Figma, take relevant online courses, practice with small projects, and join online AI design communities for additional insights and support. This approach offers both theoretical understanding and practical experience.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
AI-generated design suggestions provide valuable inspiration and efficiency, yet their reliability varies. These tools are adept at generating various ideas and analyzing data for user preferences and trends. However, they may fall short in understanding a design brief's context and cultural nuances.
It's crucial to use AI suggestions as a starting point for optimal results, with human designers adding refinement and contextual understanding. It's also important to be aware of and address potential biases in AI-generated designs. In essence, AI tools should be seen as a tool to augment rather than replace human creativity in the design process.
Take our AI for Designers course to learn more about AI.
Remember, the more you learn about design, the more you make yourself valuable.
Improve your UX / UI Design skills and grow your career! Join IxDF now!
You earned your gift with a perfect score! Let us send it to you.
We've emailed your gift to name@email.com.
Improve your UX / UI Design skills and grow your career! Join IxDF now!
Here's the entire UX literature on AI Prompts by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Take a deep dive into AI Prompts with our course AI for Designers .
Master complex skills effortlessly with proven best practices and toolkits directly from the world's top design experts. Meet your experts for this course:
Ioana Teleanu: Founder of UX Goodies and former Lead Product Designer (AI) at Miro.
Rafael Hernandez: Lead Product Designer at T. Rowe Price.
Jarvis Moore: Senior Design Lead, Design Systems at Microsoft.
Niwal Sheikh: Product Design Lead at Netflix.
Vitaly Friedman: Senior UX Consultant for the European Parliament, and Creative Lead, Smashing Magazine.
Pablo Stanley: Designer and CEO of Musho and Lummi.

We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge. Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change, , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge!
